|
Towards the Reinstatement of Absolute Space:
Some Possible Cosmological Implications
-- Héctor A Múnera
This paper reviews empirical evidences from several optical experiments on the earth showing the possiblility to detect
the motion of the Earth. Four different experiments with different technical means, and from widely separated places in
time and space, point towards solar motion in a plane with right ascension of 75º. However, there is no agreement on
the declination, which seems to be large. This evidence contradicts the widely accepted heuristic principle that the motion
of the Earth cannot be detected by terrestrial experiments, and opens the door for a reinstatement of the currently
forbidden concept of absolute space S. A closed finite Newtonian universe has interesting cosmological implications, as
compatibility with the variation of speed with distance (without expansion), and the appearance of new acceleration term of the
same order of magnitude as the Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) cut-off, thus offering an alternative explanation to
the dark matter and MOND hypotheses.
© 2009 IUP. All Rights Reserved.
The Identical Physical and Geometrical Sense
of Transformations of Galileo and Lorentz
-- Nikolai V Mitskievich
The idea of unification of space and time was first proposed by d'Alembert in 1754, while the Galilean transformation
was already given by Newton. As a synthesis of these ideas, the author elementarily deduces the standard form of
Lorentz transformation using the complementarity of coordinates and their axes under coordinates' transformations in
general. The Galilean transformation in this sense is equivalent to the Lorentz one, only being its non-orthonormalized version.
© 2009 Nikolai V Mitskievich. All Rights Reserved.
Electromagnetic Field:
Its Existence and Distinctions in Spacetimes of
Different Dimensionalities
-- Nikolai V Mitskievich
It is shown that the Maxwellian-type electromagnetic field possesses a vector potential only
in the D = 4 spacetime. In other numbers of dimensions, it either has an ( r = D/2-1) form potential, or when D is an odd number, does not exist at all. When it exists, it belongs
to intrinsically relativistic fields, which do not admit any non-relativistic approximation. Other r-form fields are also discussed, including those which model perfect fluids in the
field-theoretical language.
© 2009 Nikolai V Mitskievich. All Rights Reserved.
Inevitability of Relativistic Generalization
of the Inertial Versus Gravitational
Mass Equivalence Principle
-- Nikolai V Mitskievich
The Newtonian approximation for the gravitational field equation does not necessarily involve admission of
non-relativistic properties of the source terms in Einstein's equations. It is sufficient to merely consider the weak-field condition for
a gravitational field. When a source has electromagnetic nature, one simply cannot ignore its intrinsically relativistic
properties, since any non-relativistic approximation, which would describe electromagnetic stress-energy-momentum
complex adequately, cannot be invented. But the test particle on which gravitational field of the source is acting, should be
treated as non-relativistic.
© 2009 Nikolai V Mitskievich. All Rights Reserved.
Relativistic Invariance
-- W W Zachary and Tepper L Gill
A modification of the conventional Maxwell theory of electrodynamics is constructed by replacing the observer-time by
the proper-time of the source. This formulation is mathematically, but not physically, equivalent to the conventional
formulation. The change induces a new symmetry group that is distinct from, but closely related to, the Lorentz group and fixes the
clock of the source for all observers. The new wave equation contains an additional dissipative term that arises instantaneously
with acceleration. This shows that the origin of radiation reaction is not the action of a charge on itself, but arises from
inertial resistance to changes in motion. This dissipative term is equivalent to an effective mass, so that classical radiation has
both a massless and a massive part. Hence, at the local level, the theory is one of particles and fields, but there exists no
self-energy divergence (nor any of the other problems with which the conventional theory is afflicted). It is also shown that, for any
closed system of particles, there exists, for each observer, a global inertial frame and a unique invariant global proper-time
from which the system may be observed. This global clock is intrinsically related to the proper clocks of the individual particles
and provides a unique definition of simultaneity for all events associated with the system.
We suggest that this global clock is the historical clock, discussed by Horwitz and Piron
(1973) and Fanchi (1993a and 1993b). The theory is of the
action-at-a-distance type and the absorption hypothesis of Wheeler and Feynman follows from global conservation of energy. The present
theory is analogous to theirs, but we do not use advanced fields.
© 2009 IUP. All Rights Reserved.
Torsion and Axial Current
-- Prasanta Mahato
The role of torsion and a scalar field 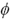 in gravitation, especially, in the presence of a Dirac field
in the background of a particular class of the Riemann-Cartan geometry is considered
here. Recently, a Lagrangian density with Lagrange multipliers has been proposed, which has
been obtained by picking some particular terms from the SO (4, 1) Pontryagin density, where
the scalar field in gravitation, especially, in the presence of a Dirac field
in the background of a particular class of the Riemann-Cartan geometry is considered
here. Recently, a Lagrangian density with Lagrange multipliers has been proposed, which has
been obtained by picking some particular terms from the SO (4, 1) Pontryagin density, where
the scalar field 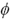 causes the de Sitter connection to have the proper dimension of a gauge field.
In this formalism, conserved axial vector matter current can be constructed, irrespective of
any gauge choice, in any space-time manifold having arbitrary background geometry. This
current is not a Noether current. causes the de Sitter connection to have the proper dimension of a gauge field.
In this formalism, conserved axial vector matter current can be constructed, irrespective of
any gauge choice, in any space-time manifold having arbitrary background geometry. This
current is not a Noether current.
© 2009 IUP. All Rights Reserved.
The Symmetries C , P and T of the Dirac Field and Their Non-Relativistic Limit
-- Dalia Cervantes C
Initially, we found a bundle, which contains the matrix representation of
the transformations C, P, T and for the Dirac field and we studied their action on the elements of the Dirac algebra D16.
We give a geometrical description of the action of the parity on non-relativistic 1/2 spin
Pauli spinors in terms of the bundle theory. The relevant bundle, which contains the matrix representation of
the transformations C, P, T and for the Dirac field and we studied their action on the elements of the Dirac algebra D16.
We give a geometrical description of the action of the parity on non-relativistic 1/2 spin
Pauli spinors in terms of the bundle theory. The relevant bundle,  is a non-trivial extension of the universal covering group is a non-trivial extension of the universal covering group  . From the direct product of O(3) by Z2 naturally induced by the structure of Galilean group, we identify, in its double
cover, the time reversal operator . From the direct product of O(3) by Z2 naturally induced by the structure of Galilean group, we identify, in its double
cover, the time reversal operator  acting on spinors, and its product with acting on spinors, and its product with  . At the end, we study the non-relativistic limit of
the charge conjugation transformation C in the context of the Dirac equation coupled to an electromagnetic field.
The existence of these limits is supported by the consistence between the `large' and `small' components for the spinor
and the conjugate spinor respectively and by an argument based in the quantum field theory. Finally, if one complexifies
the Lorentz group, and therefore, the Galilean spacetime, the explicit form of the matrix for
allows C to interpret it, in this context, as the complex conjugation of the spatial coordinates . At the end, we study the non-relativistic limit of
the charge conjugation transformation C in the context of the Dirac equation coupled to an electromagnetic field.
The existence of these limits is supported by the consistence between the `large' and `small' components for the spinor
and the conjugate spinor respectively and by an argument based in the quantum field theory. Finally, if one complexifies
the Lorentz group, and therefore, the Galilean spacetime, the explicit form of the matrix for
allows C to interpret it, in this context, as the complex conjugation of the spatial coordinates  . This result is natural in a fiber bundle description. . This result is natural in a fiber bundle description.
© 2009 Dalia Cervantes. All Rights Reserved.
On Completion
of Einstein's Unified Field Theory
-- Mendel Sachs
The author's research program over the past 50 years has dealt with a generalization of the expression of the theory
of general relativity, within its own logical base, and its application to problems of cosmology, astrophysics and
particle physics. One part of this program was to show that a generalized version of the theory yields the formal structure
of quantum mechanics as a linear approximation for a generally covariant field theory of the inertia of matter
(Sachs, 1986). The second part of this program was to demonstrate that the generalized version of general relativity
yields a unified field theory of gravitation and electromagnetism, in terms of a single field (Sachs, 1982). This paper is devoted
to the latter, demonstrating a unified field theory within the confines of the logical basis of the theory of general relativity.
© 2009 IUP. All Rights Reserved.
Quantum Corrections in N = 1 Supersymmetric
Theories: Is Everything Clear?
-- K V Stepanyantz
This paper discusses some interesting features of quantum corrections in N = 1 supersymmetric theories, which have
been discovered analyzing calculations made with the higher covariant derivative regularization. In particular, the author
argues that all integrals, defining the Gell-Mann-Low function in supersymmetric theories, are integrals of total derivatives. As
a consequence, possibly there are some interesting identities, which restrict Green functions and do not follow from
usual Slavnov-Taylor identities.
© 2009 IUP. All Rights Reserved.
Mirror Dark Matter Discovered?
-- Z K Silagadze
Recent astrophysical data indicates that dark matter shows a controversial behavior in galaxy cluster collisions. In case
of the notorious bullet cluster, dark matter component of the cluster behaves like a collisionless system. However, its
behavior in the Abell 520 cluster indicates a significant self-interaction cross-section. It is hard for the Weakly Interacting
Massive Particles (WIMP) based dark matter models to reconcile such a diverse behavior. Mirror dark matter models, on
the contrary, are more flexible and for them diverse behavior of the dark matter is a natural expectation.
© 2009 Z K Silagadze. All Rights Reserved.
Dark Matter from Stable Charged Particles?
-- Maxim Yu Khlopov
Particle physics candidates for cosmological dark matter are usually considered as neutral and weakly interacting.
However, stable charged leptons and quarks can also exist and, hidden in elusive atoms, play the role of dark matter. The
necessary condition for such scenario is the absence of stable particles with charge -1 and effective mechanism for suppression
of free positively charged heavy species. These conditions are realized in several recently developed scenarios. In a
scenario based on the walking technicolor model, excess of stable particles with charge -2 and the corresponding dark
matter density is naturally related with the value and sign of cosmological baryon asymmetry. The excessive charged particles
are bound with primordial helium in techni-O-helium `atoms', maintaining specific nuclear-interacting form of dark
matter. Some properties of techni-O-helium universe are discussed.
© 2009 IUP. All Rights Reserved.
State, Statistics and Quantization in Einstein's
1907 Paper, `Planck's Theory of Radiation and
the Theory of Specific Heat of Solids'
-- Peter Enders
Einstein's paper, "Planck's Theory of Radiation and the Theory of Specific Heat of Solids" (1907) is famous for that it
marks the beginning of the quantum theory of solids. In contrast to classical statistics, a simple quantum oscillator model
of lattice vibrations yields a decreasing specific heat with decreasing temperature, in agreement with the then few
experimental findings. This brought him to the attention of Nernst, who became one of the driving forces to attract Einstein to
Berlin. Less known is, however, that this paper contains two other fundamental insights. First, it shows that the
differences between classical and quantum statistical distribution functions are related to the energetic spectra of systems,
rather than to the (in)distinguishability of particles. Second, the problem of quantization is (indirectly) formulated as the
problem to select the set of quantum states out of the set of classical states. Such an approach allows to satisfy the
requirements of any quantization posed by
SchrÖdinger as early as 1926. Nevertheless, this paper has found much less attention
than most other pioneering contributions by Einstein. It is hoped that the revival of these thoughts will help to overcome
some of the still present difficulties in the interpretation of quantum mechanics as well as to provide a dynamical solution
to Gibbs' paradox within classical statistical mechanics.
© 2009 IUP. All Rights Reserved.
|


