In the recent wireless communication system, the use of microstrip antennas
has become popular because of their significant merits like planar, ease of
integrability, fabrication, small size, low cost and light weight. The field of application of
these antennas is restricted by few of their limitations such as larger size at lower
frequencies (importability), narrow bandwidth, low gain and high cross-polarization.
Several techniques are available in the literature to overcome these limitations such as
use of various feeding techniques (Mohammed et
al., 2009), use of multilayer structures (Zehforoosh et al., 2006), use of array elements (Levine et al., 1989) and use of slot (See and Zhi, 2002), etc. In this study, a novel geometry of Modified Ground
plane Complementary-Symmetry Microstrip Antenna (MGCSMA) is proposed which is
simple and uses a single substrate material. This antenna is fed through microstrip line
feed which can be fabricated simultaneously along with the patch element. The
proposed method considerably improves the number of antenna parameters together.
The presented antennas are designed using low cost glass epoxy substrate
material of thickness d = 1.66 mm and permittivity 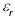 = 4.2. The artwork of these
antennas is sketched using computer software Auto-CAD 2006 to achieve better accuracy.
The antennas are fabricated using photolithography process. = 4.2. The artwork of these
antennas is sketched using computer software Auto-CAD 2006 to achieve better accuracy.
The antennas are fabricated using photolithography process.
Figure 1 shows the top view geometry of Conventional Rectangular
Microstrip Antenna (CRMA) with tight ground plane shielding. The CRMA is designed using
the equations available in the literature (Bahl and Bhartia, 1980) for 4 GHz of
frequency. The length and width of the rectangular patch are Lp and Wp respectively. The
feed arrangement consists of quarter wave transformer of length Lt and width Wt which is connected as a matching network between the patch and the microstrip line
feed of length L50 and width W50. |





