
October'23
The IUP Journal of Organizational Behavior
Archives
How HR Analytics Can Help Improve Decision-Making, HR Practices and Firm Performance: A Systematic Review
Mansi
Research Scholar, Department of Management, Central University of Rajasthan, Ajmer, Rajasthan, India. E-mail: rai.mansi777@gmail.com
Tulsee Giri Goswami
Assistant Professor, Department of Management, Central University of Rajasthan, Ajmer, Rajasthan, India; and is the corresponding author. E-mail: tulseegoswami@curaj.ac.in
Human Resource (HR) analytics is the process of collecting and analyzing employee data to understand the association between HR practices and firm performance to make decisions and formulate strategies. The study aims to systematically evaluate the literature on HR analytics under three aspects: decision-making, performance, and HR practices and functions. For this purpose, the study systematically reviews the literature on HR analytics available on Web of Science database. The study reviews 43 papers relating to HR analytics and finds decision-making as the building block for various effective HR practices and for enhancing the performance of employees. With regard to other available HR practices, organizations view recruitment and selection, retention, turnover, training, and employee engagement as crucial. These are the areas where management uses HR analytics for tackling big data and improving performance. The study further highlights the value addition HR analytics provides. By analyzing the interconnections between various factors through co-occurrence network analysis, the study shows that the importance management attaches to workforce data (through effective HR practices) while making strategic decisions plays a crucial role in enhancing the performance of the organization.
From being operational in the 19th century to strategic in the early 20th century, human resource management (HRM) has become data-driven. The wave of big data has left no organizations with no choice of putting off its use to the future. The evolution of HRM from metrics to big data is through HR analytics (Garcia-arroyo and Osca, 2019). HR analytics is when an organization collects its human resource data and analyzes it to understand the connection between HR practices and organizational performance to make decisions and strategies. Analytics is mainly categorized into descriptive (what has happened), predictive (what will happen), and prescriptive analytics (what should be done) (Nagpal and Mishra, 2021).
The categories facilitate data-driven decision-making by applying statistical modeling to HR-related data. Although HR analytics and people analytics are the most famous, they are the same as workforce analytics, human capital analytics, and talent analytics. A trend study by Society for Information Management (SIM) identified analytics as the organization's largest IT investment area (Kappelman et al., 2020). Despite trending, the adoption rate of analytics in the HR domain could be higher (Marler and Boudreau, 2017).
Even before implementing analytics, understanding the vital role of workforce's contribution to organizational success is essential for organizations (King, 2016). HR has an inside/outside approach and a purpose of adding value to the organization (Ulrich and Dulebohn, 2015). The workforce data analysis aids the organization in understanding the employees working in the organization better. Organizations use analytics to gather data on productivity, absenteeism, job satisfaction, and engagement, which helps them formulate recruitment, retention, training, fulfilment, compensation, and engagement strategies. However, this technology extends beyond recruitment to performance management, succession planning, and employee engagement. Few studies have explored HR analytics' impact on succession planning, performance management, and employee engagement, indicating a potential gap in understanding its potential for optimizing HR practices.
HR analytics is a crucial investment domain that enhances HR decision-making by providing management with facts, information, and evidence, prioritizing people and justifying decisions. Therefore, researchers need to explore HR analytics' impact on organizational decision-making, as understanding this influence is crucial for optimizing HR strategies and ensuring data-driven decision-making. Based on this, the first research question formulated is as follows:
RQ1. How much does HR analytics aid in the decision-making of the organization?
Under the umbrella of human resource management, HR analytics is gaining interest as an innovative, strategic, and practical decision-making approach. Moreover, big data analytics also significantly impacts employee selection and recruitment, organizational decision-making, performance management (McAbee et al., 2016), and talent management, as noted by Margherita (2022) and Prokesch (2017). Despite the significant advancements in analytics, there still needs to be a significant gap in understanding the role of HR analytics in HR practices. Thus, this paper aims to contribute to the existing literature on the association between HR analytics and organizational outcomes. With relevance to this, the second research question drafted is as follows:
RQ2. What HR practices are carried out using HR analytics in an organization, and how has HR analytics transformed them?
With a significant influence on functional and strategic decision-making, HR analytics can be seen as an increasingly established discipline that has a documented impact on business outcomes (Margherita, 2022; Van den Heuvel and Bondarouk, 2017). The studies by Holwerda (2021), McCartney and Fu (2022), Wang and Cotton (2017) have documented the performance aspect of HR analytics. The study highlights a gap in understanding the holistic impact of HR analytics on a firm's performance, highlighting the need for further research to understand how HR analytics aligns with strategic goals and drives competitive advantage. Based on this research gap, the third research question is framed as follows:
RQ3. How does HR analytics influence the firm's performance?
Hence, the paper focuses on the association between HR analytics and decision-making, HR practices, and performance aspects by systematically reviewing the literature available on Web of Science database.
Data and Methodology
Identification
The data is collected from the Web of Science (WoS) database, an all-inclusive educational resource comprising more than 8700+ core academic journals (Hanisch and Wald, 2008). Prior studies have been reviewed to determine the appropriate keywords for this study. The search query, keeping in mind the scope of the study, is set as 'Human Resource Analytics', 'People Analytics', 'Talent Analytics', or 'Workforce Analytics'. The mentioned information was searched in the 'ALL' field of the Web of Science database, ((ALL = (Human Resource Analytics)) OR ALL = (People Analytics) OR ALL = (Talent Analytics) OR ALL = (Workforce analytics)), and an initial list of 2679 papers appeared.
Screening
Web of Science comprises 250 subjects in science, arts and humanities, and social sciences. However, the data was limited to only management, business, business finance, and social science interdisciplinary categories, yielding 343 papers without specifying the period.
Eligibility
In the third step, after carefully studying the title and abstract, the papers were refined to 143, and all works irrelevant to HR analytics were removed.
Inclusion
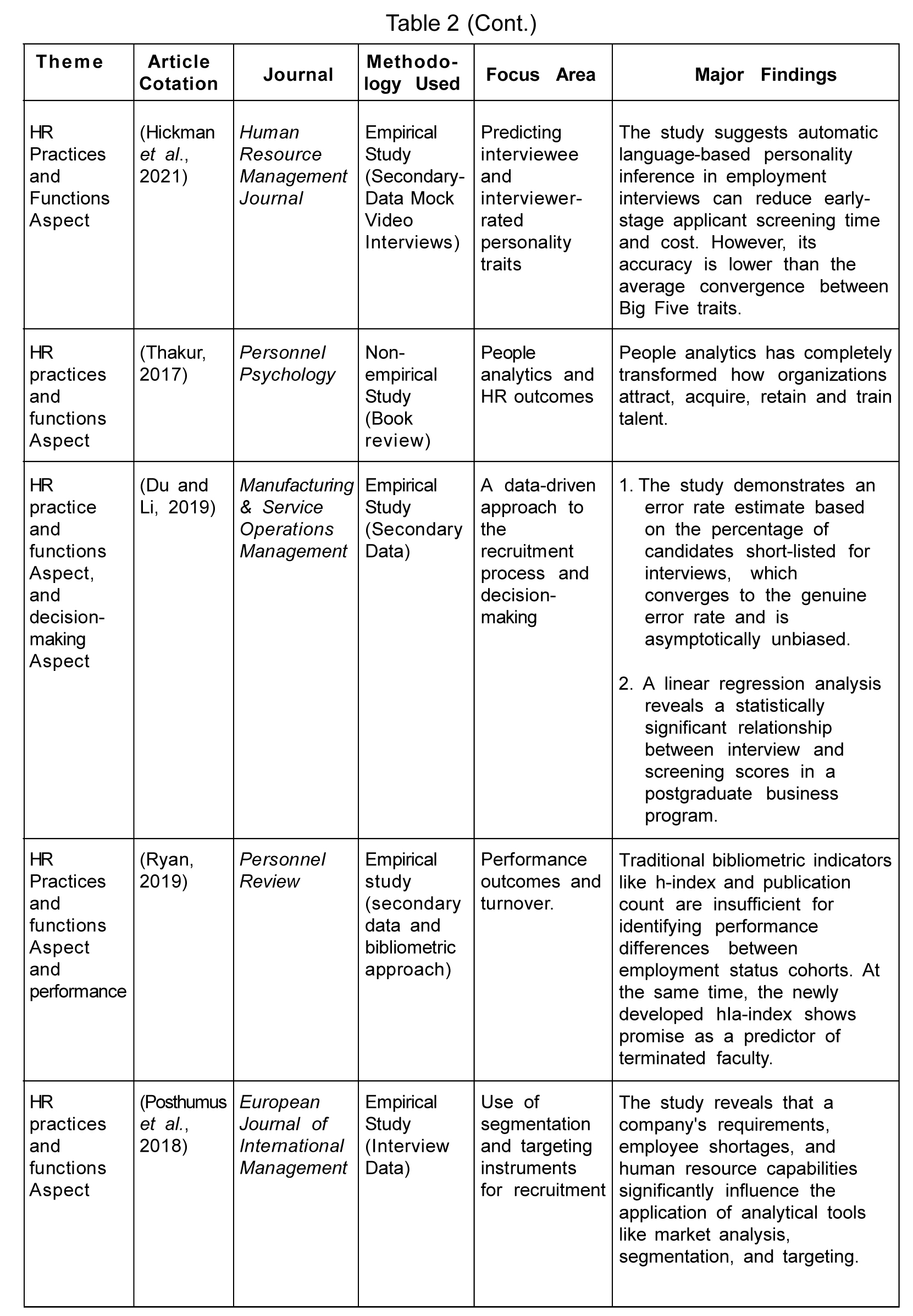
To effectively collect data relating to HR analytics, concerning decision-making, HR practices, and performance aspects, the study scrutinized each paper's title, abstract, and conclusion. Finally, 43 papers were selected for analysis (Figure 1).
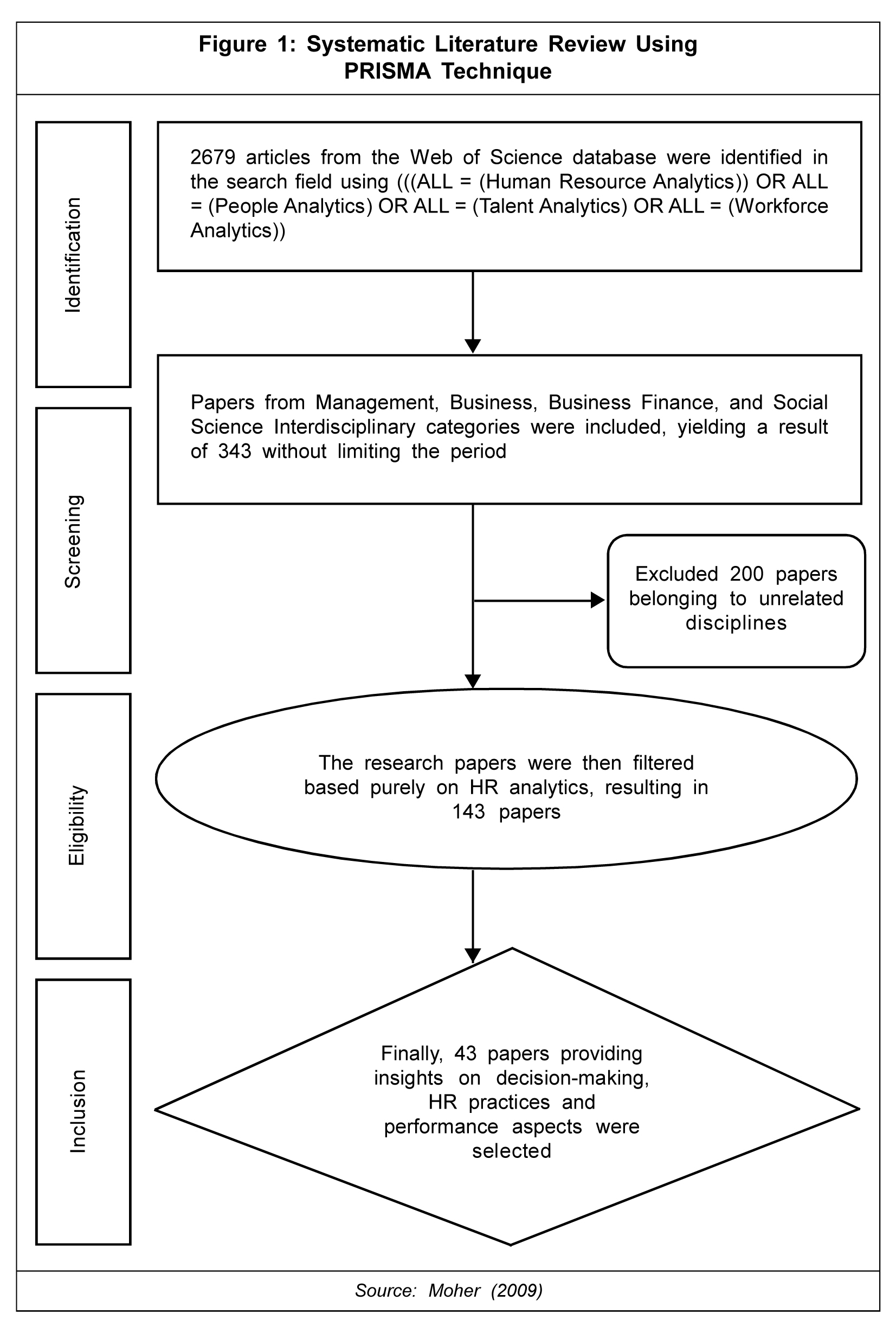
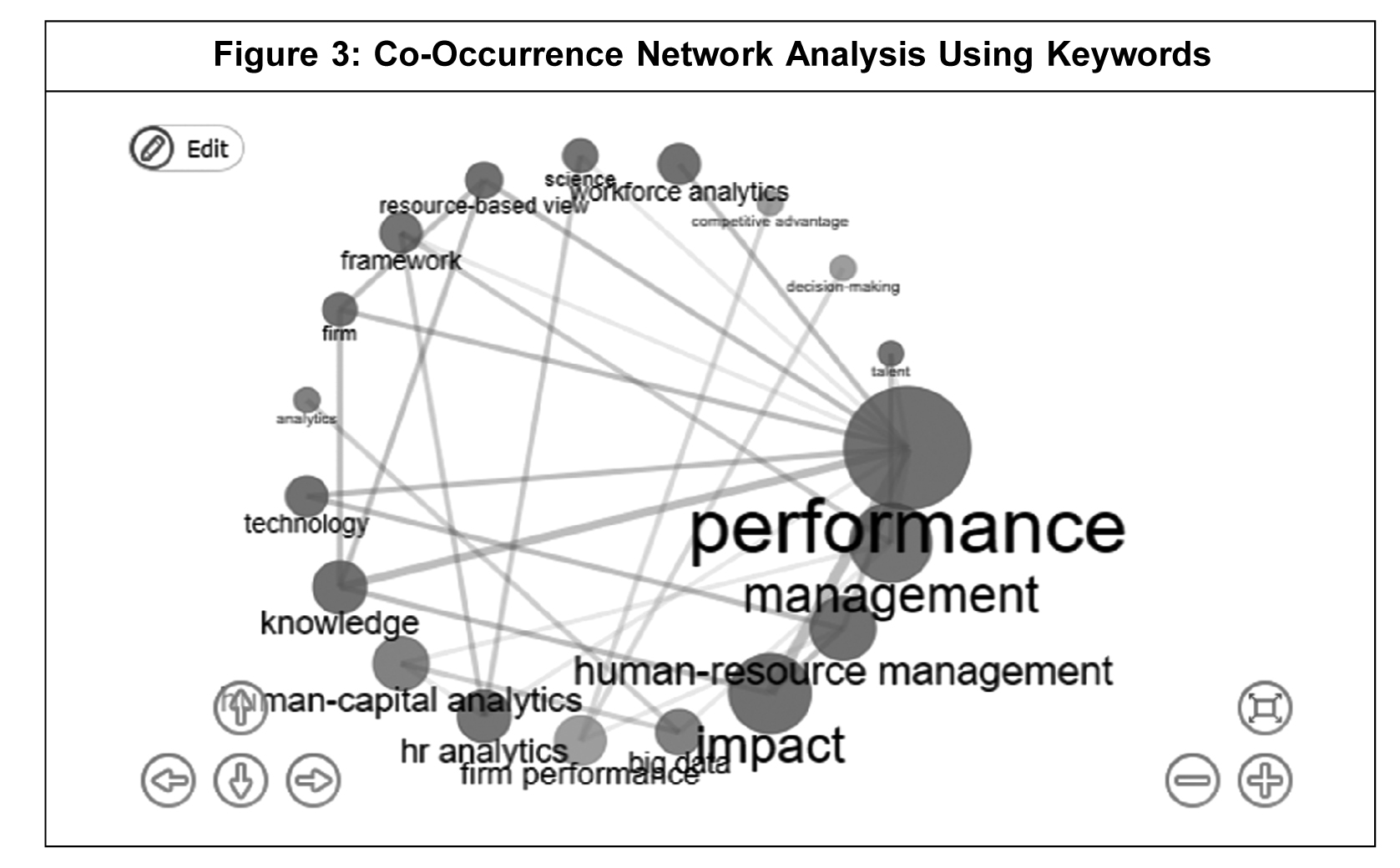
This paper follows systematic literature review technique to identify the problem of research. Moreover, using 'R' software (bibliophile), this paper provides insights on descriptive analysis, word cloud analysis, and co-occurrence network analysis. Furthermore, the utilization of co-occurrence network analysis in this study aids in providing a quantitative approach to validate the relationship between competitive advantage (through effective HR practices), decision-making, and firm performance.
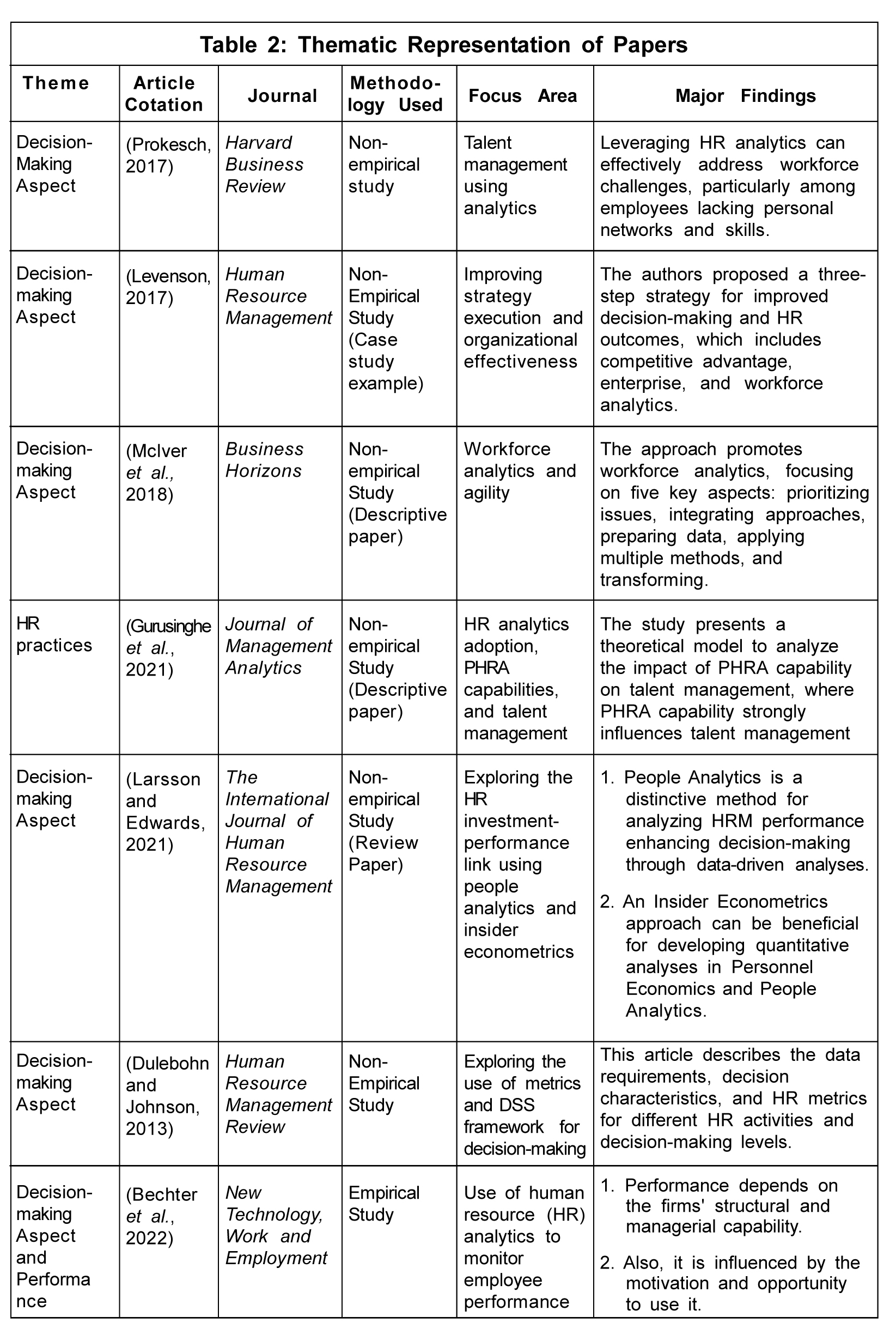
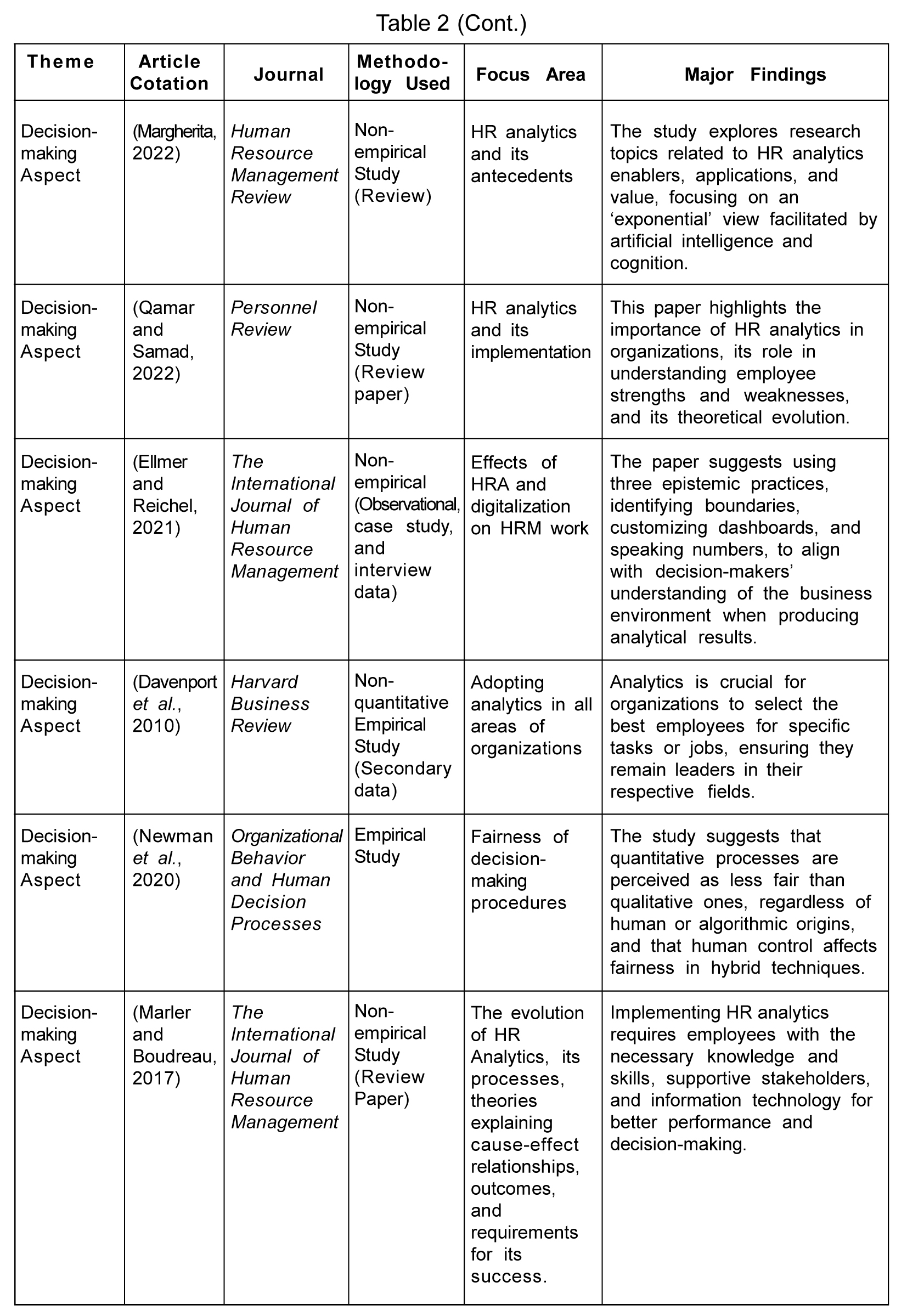
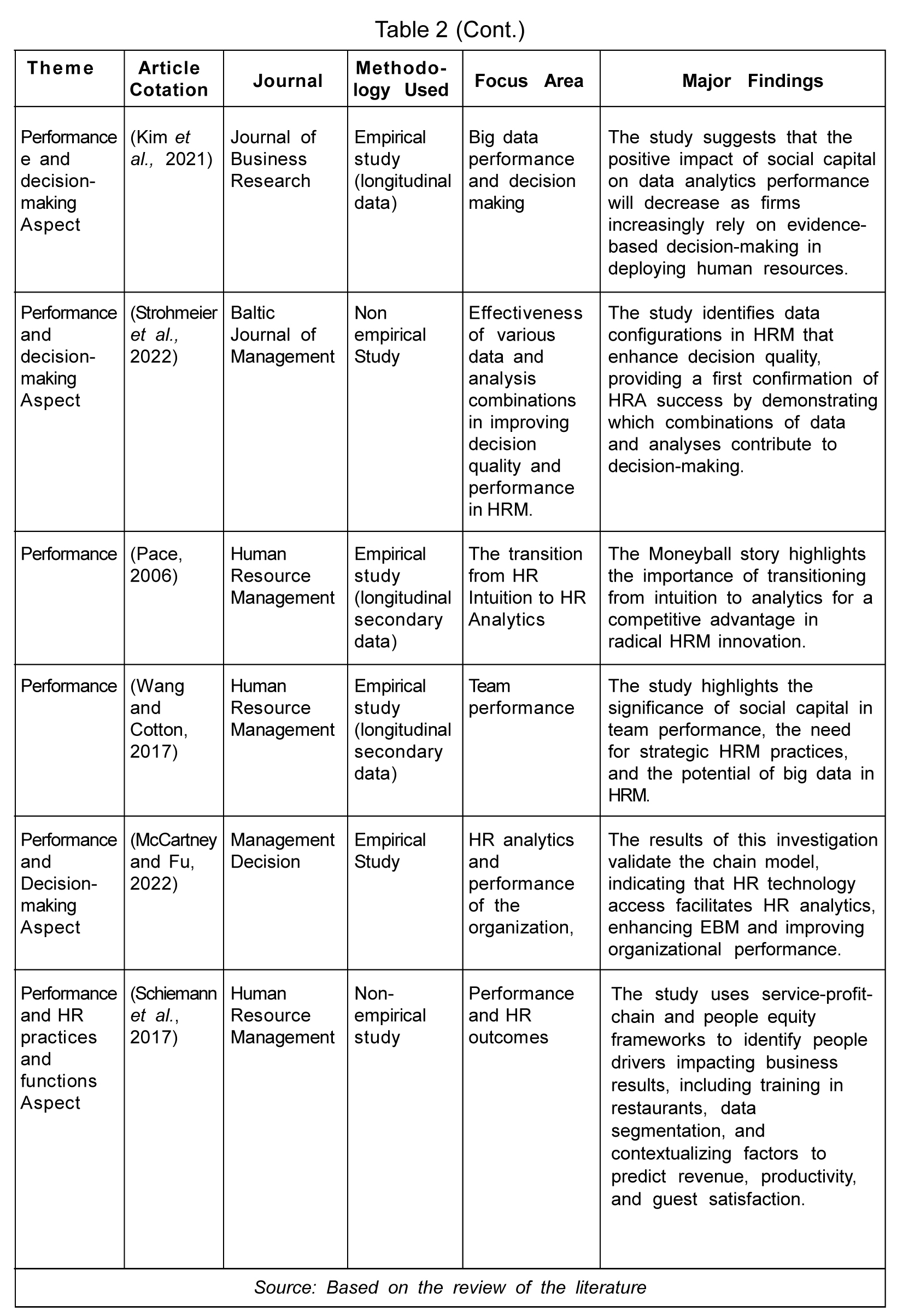
HR Analytics and Decision-Making
One of the objectives of this paper is to find out how many studies have highlighted the importance of analytics for effective HR decision-making is. The decision-making task in an organization is a massive responsibility on the shoulders of management. By making informed judgments, managers may show employees that they value their work and care about their best interests. Ben-gal (2019) also identified decision-making as one of the four major trends in HR analytics. Several authors like Gurusinghe et al. (2021), Larsson and Edwards (2021), Levenson (2017), and Mclver et al. (2018) have explained the use of HR analytics for better strategy execution in various studies. Using a Decision Support System (DSS) and Business Intelligence supports organizations' complex decision-making and offers multiple opportunities to solve vital HR problems (Dulebohn and Johnson, 2013). Providing the management with strategic information, HR analytics changes the whole scenario for decision-makers.
Every organization's primary purpose behind these analytical information tools is to enhance decision-making effectiveness and provide timely, valid, reliable data to support HR decision-making (Marler and Boudreau, 2017). HR analytics provides analytical outputs that add value to an organization's decision-making (Bechter et al., 2022; and Margherita, 2022). Ellmer and Reichel (2021) used the 'HRM-as-practice' approach to discover the techniques for rendering HRA-pertinent outputs for decision-making. Shamim et al. (2018) stated that an organization's extensive data in decision-making capabilities include talent management, organizational culture, leadership, and technology. According to Davenport et al. (2010), talent analytics aids management while answering six significant queries: key indicators, attention-required areas, workforce forecast, talent supply chain, talent value model, and people investment analysis.
Using algorithms, analytics, and metrics leaves zero scope for subjectivity in decision-making. At the same time, some argue that the elimination of biases leaves certain qualitative information unevaluated. Newman et al. (2020) also highlighted how decision-making may stress too much on the quantitative aspect, ignoring the qualitative aspect of employees. Organizations that leverage analytics can make decisions based on evidence that improves the workforce and the organization.
HR Analytics and HR Practices
Organizations' transforming HR functioning with technology has led to the emergence of e-HR (Dulebohn and Johnson, 2013; and Gurusinghe et al., 2021). The e-HR approach allows organizations to pile, represent, and utilize data to support HR functions in an organization. Various HR practices and functions (i.e., recruitment and selection, talent management, training, and employee engagement) have gained attention from scholars.
The process of recruitment can be supported by evidence-based decision-making through HR analytics. For mass recruitment, organizations need less time-consuming methods that reduce workload, such as language-based algorithms (Hickman et al., 2021). People analytics also has the potential to influence the planning, hiring, and changing of the behavior of employees (Thakur, 2017). Du and Li (2019) presented a method for calculating the error rate in which the likelihood of a candidate getting rejected in the recruitment process is compared to the median job performance of those who are accepted. Ryan (2019) examined the faculty turnover, mobility, and performance in a university, taking into account the hIa-index instead of the h-index, a bibliometric indicator for research performance comparison by applying ANOVA, and described how organizations could use this as an HR analytics tool for decision-making. Also, according to Posthumus et al. (2018), analyzing the market data along with the instruments of segmentation and targeting for recruiting employees in the pharmaceutical industry proved helpful. It also simplifies finding the best sources for recruiting, evaluates candidate fit, and forecasts candidate success using past performance data.
Identifying training needs, intervals, and quantity requires an adequate understanding of the employee's needs. It also helps determine the most effective training initiatives, anticipate problems before they arise, and recognize the elements influencing employee turnover. To identify the hurdles to performance path and the reasons behind the issues, Cotes and Ugarte (2019) proposed a training need analysis in the banking field by highlighting the tactical utilization of HR analytics regardless of its importance in bringing effectiveness and efficiency to HR practices and functions for the performance of the organization.
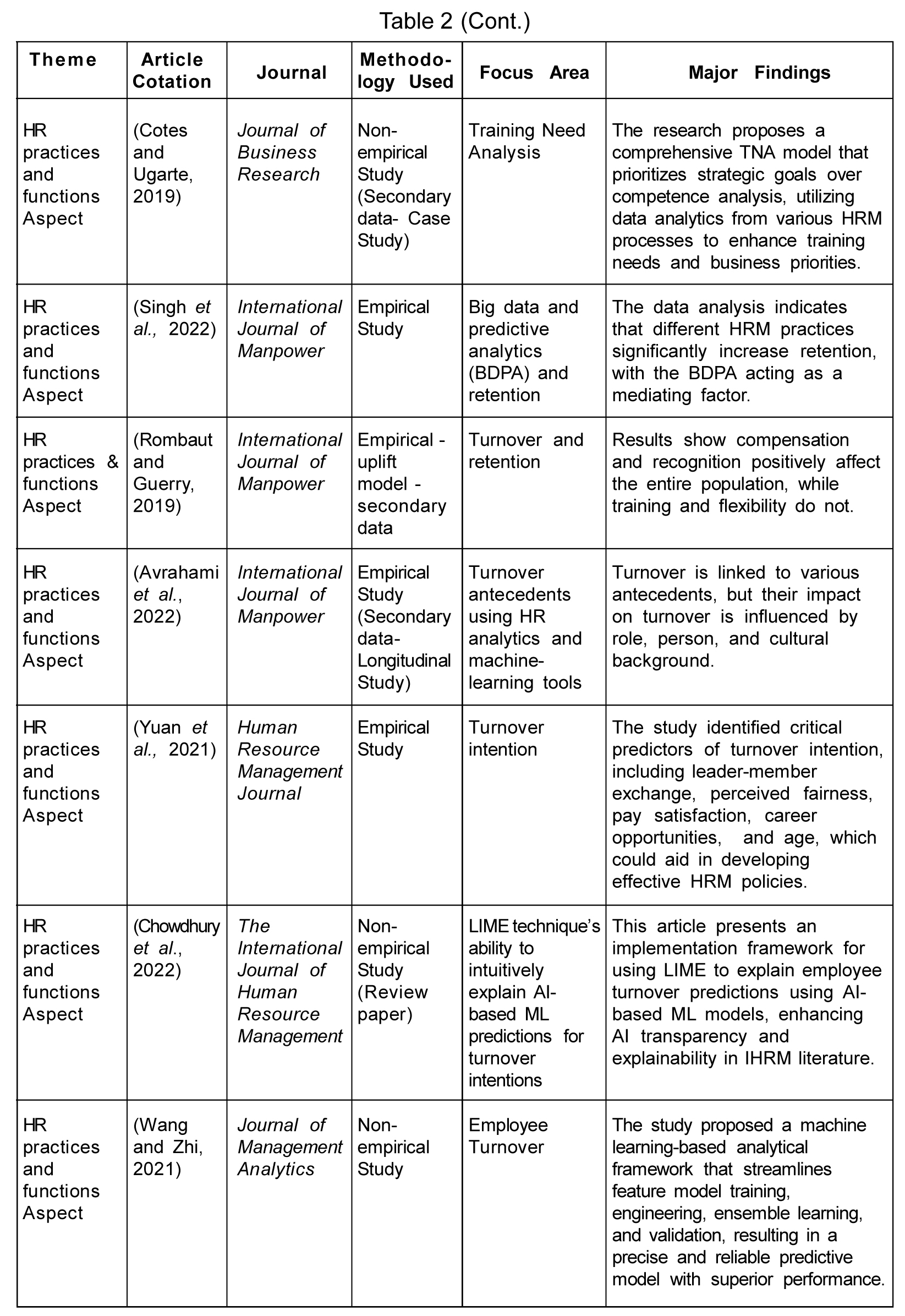
Predictive HR analytics conclusively connects to employee retention, development, and acquisition (Gurusinghe et al., 2021). According to Singh et al. (2022), the significant role of big data predictive analytics in improving the retention rate of employees under the mediation effect is crucial. HR practices such as remuneration and reward, grievance handling, recruitment and selection, performance and career development, training and development, and employee involvement positively and significantly affect employee retention rates (Singh et al., 2022). Rombaut and Guerry (2019) analyzed the effect of employee retention strategies on employee turnover through a data-driven approach and found compensation and recognition to impact employee turnover significantly. However, the need for more understanding about the processing and storage of data related to employees creates issues in the retention of employees.
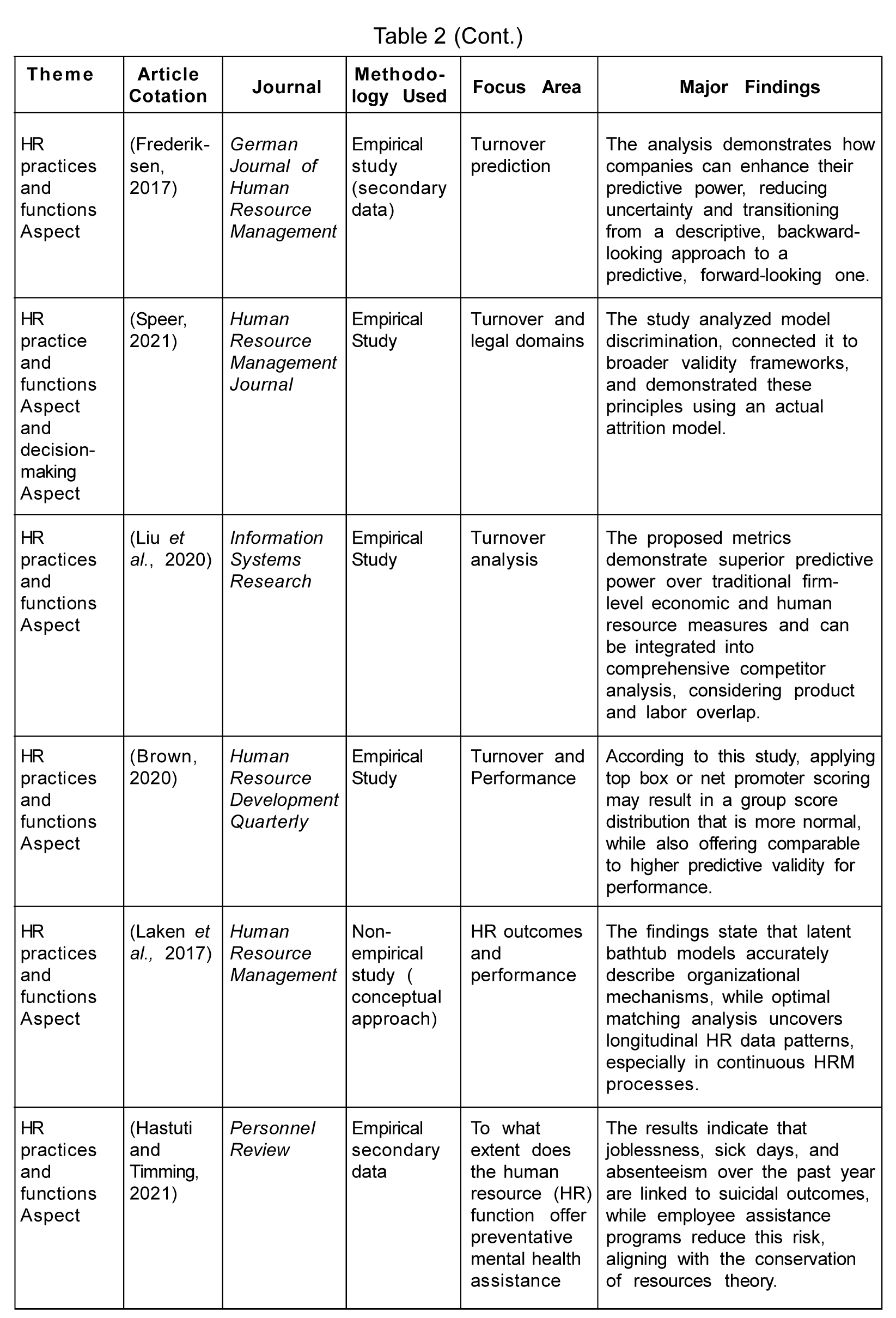
HR analytics can be a supporting tool for predicting employee turnover if used wisely by organizational management (Wright, 2017). Avrahami et al. (2022) revealed that turnover association with levels of antecedents such as competencies, cultural values, commitment, and trust is contingent upon the organization's role, person, and culture. According to Yuan et al. (2021), career opportunities, perceived fairness, age, pay satisfaction, and leader-member exchange predicts turnover intention. HR analytics can help with better business planning, risk mitigation, and adaptability to changes in the business environment by anticipating future workforce needs. Organizations use artificial intelligence-based machine learning models like Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations (LIME) technique to understand the reasons behind the predicted employee turnover (Chowdhury et al., 2022). Another machine-based analytical framework for the robust prediction of employee turnover has been developed by Wang and Zhi (2021). According to Frederiksen (2017), organizations move from descriptive to prescriptive HR analytics by analyzing job satisfaction data to predict turnover. HR analytics is a data-analytical tool that aids in assessing compensation patterns, maintaining competitive benefits and compensation, and evaluating the success of diversity and inclusion initiatives. Speer (2021) outlined a three-step process of removing or altering variables if they negatively impact diversity goals (attrition and validity) before implementing the attrition model. HR analytics traces the human capital flow across organizations through human capital overlap metrics by performing interfirm labor market competitor analysis using employee migration information (Liu et al., 2020).
Hastuti and Timing (2021) found the association between joblessness, absenteeism, sick days, and suicidal outcomes to be a significant one. Therefore, measuring employees' attitudes, opinions, and feedback is vital to the organization for effective management of employees, which calls for optimal methods for reporting and rating survey results. The net promoter employee engagement metric proved the most effective, yielding more productive work outcomes and greater predictive performance validity (Brown, 2020). HRM focuses on making evidence-based decisions regarding human capital in the organization, which requires statistical methods to be applied to HRM.
Laken et al. (2017) proposed, using the bathtub model and optimal matching analysis, to unveil the longitudinal patterns in HR data concerning their management. They showed how these have added value to the management practice of employee engagement and career pattern analysis. To summarize, HR analytics has revolutionized conventional HR practices by providing a data-driven/analytical approach to decision-making, improving HR practices and functions overall, and bolstering organizational goals.
HR Analytics and Performance
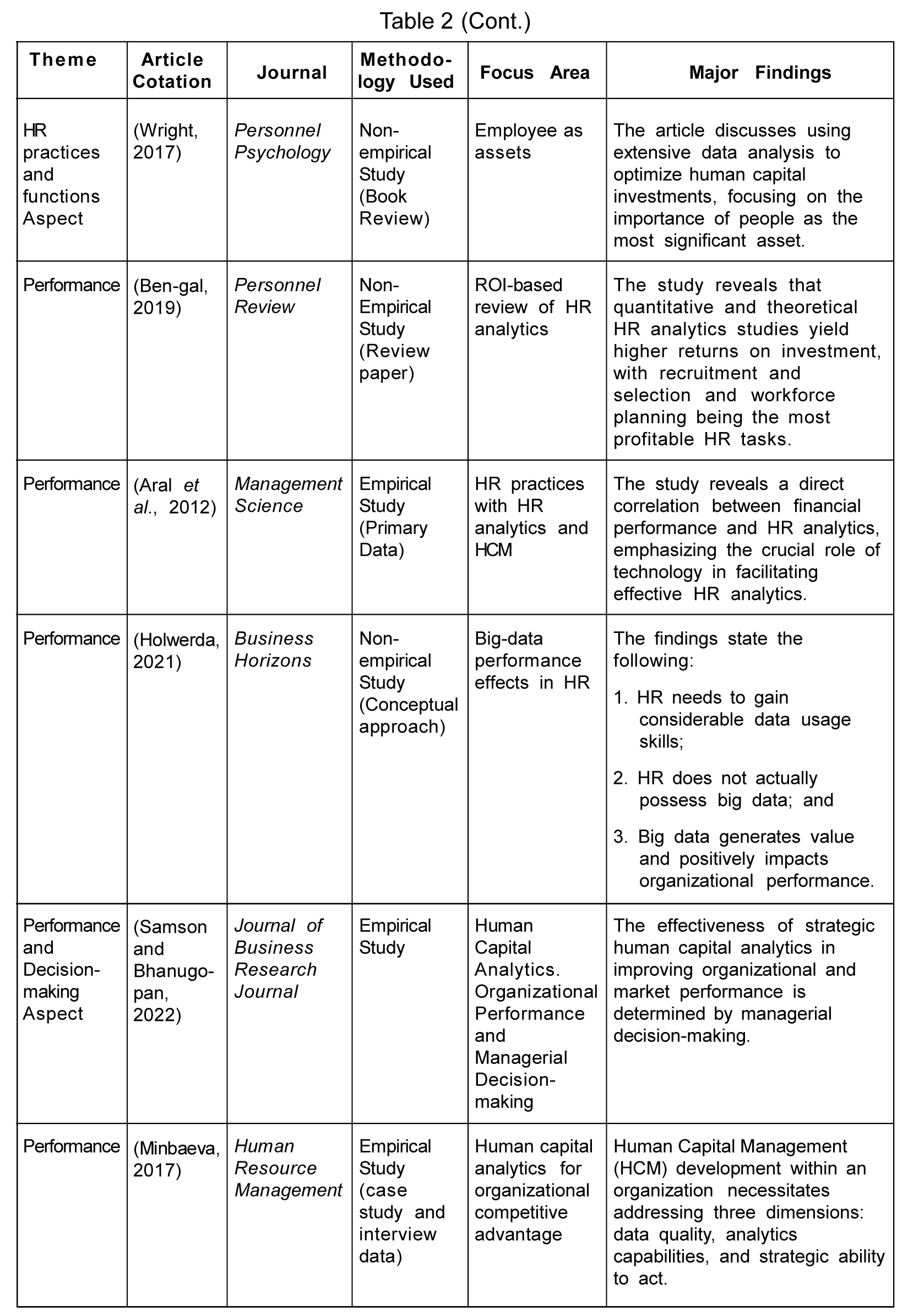
The transition of HR from intuition-based to analytics-based is not surprising, given the vast amount of data. The interaction between HR analytics and technology (antecedent) facilitates evidence-based management, indirectly contributing to organizational performance (McCartney and Fu, 2022). In a dynamic technological environment, employees are the only constant resource providing an organization with a competitive advantage. Organizations need help to use workforce information to remain competitive and manage resources effectively. Schiemann et al. (2017) shared the work of successful organizations using human capital and business framework, including people equity (alignment, capabilities, and engagement) and service profit chain-the alignment capabilities engagement framework aids in predicting employee turnover, revenue, profit, and customer satisfaction.
According to Minbaeva (2017), the success of HR analytics depends on three dimensions: data quality, analytics capabilities, and strategic ability to act and prove its value. An analytical officer with the role of change agent, an HRIS, and a team of miners for data mining are all that required for the successful transformation to an HR analytical organization (Pace, 2006). Wang and Cotton (2017) explained how workforce analytics brings value addition not only to the workforce but also to organizational strategy execution. The decisions regarding the changes in team membership are taken after carefully analyzing the workforce-related information. Workforce differentiation is a challenging task for the organization that can be taken care of with due respect to analytics by making a disproportionate investment in resources, development opportunities, and rewards for high performers (Becker et al., 2009). Aral et al. (2012) also recommended using HR analytics, information technology, and performance pay, for better performance and productivity. HR analytics allows organizations to understand their workforce better and have a competitive advantage over others.
Monitoring employee performance with HR analytics is dramatically determined by firm-specific factors (managerial and structural capability of the firm) (Bechter et al., 2022). According to Strohmeier et al. (2022), the better the data and analysis intensity, the more likely the business outcomes will be. Gurusinghe et al. (2021) argued that while promising decisions for upgrading employee management, predictive HR analytics amplifies organizational performance. According to Holwerda (2021), using significant data approaches in HR yields performance-based outcomes. HR analytics also aids in determining the return on investment (ROI) of learning initiatives, ensuring competitive pay structures and alignment with organizational goals. Evidence-based approach to making effective organizational decisions is possible through HR analytics. The reason behind calling it an evidence-based practice is its dependence on valid facts, data, and employee information. Critically examining analytics, Minbaeva (2020) viewed HR analytics as a hammer used for constructive and destructive purposes. At the same time, Kim et al. (2021) argued that organizations perform better by combining intuition-based and data-driven decision-making to make HR personnel decisions and have a competitive edge.
Discussion
The study provides insights into the growing discipline of HR analytics by answering the following research questions relating to decision-making, HR practices, and performance.
RQ1. How much does HR analytics aid in the decision-making of the organization?
This study systematically evaluates the decision-making aspect of HR analytics. HR analytics aids in overcoming the various management challenges for better decision-making related to strategic execution or organizational effectiveness. Organizations must understand the workforce through HR analytics for strategic decision-making to provide valuable insights. Highlighted as one of the major trends in HR analytics by Ben-gal (2019), decision-making can be considered the fundamental pillar for enhancing the organization's effectiveness and performance. Schiemann et al. (2017) stated that talent and workforce analytics can improve human and business resource decisions despite providing limited value.
Newman et al. (2020) argued about HR analytics' negative impact, leaving qualitative information and contextualization needing more evaluation. Nevertheless, the available literature needs to explain what harmful impact organizations face. Keeping in mind the negative consequences (privacy and ethical issues) analytics brings to the management; it can potentially transform the working of HRM through its strategic decision-making based on hard facts. Overall, HR analytics empowers organizations to move beyond gut feelings and subjective judgments, providing quantitative insights that enable them to identify trends, patterns, and potential areas for improvement, ultimately supporting more effective and strategic decision-making across various HR functions.
RQ2. What HR practices are carried out using HR analytics in an organization, and how has HR analytics transformed them?
Secondly, the HR practice aspect of HR analytics is analyzed. The various other HR practices and functions, such as recruitment and selection, training, retention, turnover, and employee engagement, have gained significant attention of scholars. The literature links HR practices with HR analytics by providing multiple models that assist the organization in recruiting employees, providing proper training, effectively retaining HR practices, and predicting employee turnover. The positive impact of HR analytics on HR practices must be addressed after taking into account the significant impact of recruitment and selection, training and development, remuneration and reward, grievance handling, performance and career development, and employee involvement in the retention rate of employees. This study highlights the need for more literature linking HR analytics to development, compensation and reward, and career development.
Based on the review, HR analytics can be viewed as an effective tool for conducting various HR practices. However, the management should focus on adding HR-trained experts to bridge the gap between HR theory, data experts, and the business for better results of prediction models that have been ignored. Analytics enhances the overall efficiency of HR practices and contributes to achieving organizational goals. It enables HR professionals to gain deeper insights into various aspects of workforce management, leading to more effective and strategic HR initiatives. By identifying the most effective recruitment sources, predicting candidate success, and assessing the ROI of recruitment channels, HR analytics supports organizations in making evidence-based decisions. To sum up, HR analytics has revolutionized several HR procedures by offering data-driven insights and facilitating improved planning and decision-making.
RQ3. How does HR analytics influence the firm's performance?
Finally, the performance aspect of HR analytics is discussed in the study. The performance aspect in this paper covers the organization's overall performance (financial, social, and employee). This study demonstrates the value addition qualities HR analytics brings to the table. The analysis shows that organizational performance improves with effective or strategic decision-making through HR analytics, with the linking role of evidence-based management. The quantitative research linking the organization's financial performance to HR analytics is merely less in number, as witnessed in the review. Only empirical and conceptual studies discovered a connection between HR analytics and organizational effectiveness. They are pointing toward the scarcity of research linking big data analytics and the performance of organizations (Batistic and Laken, 2019). The improved performance of human resources practices, including hiring, training, and retention, is crucial to the organization's financial wellbeing and competitive edge. By bringing strategic improvements in HRM, HR analytics directly improves managerial decisions. HR analytics is required for improving firm performance by providing data-driven insights that empower firms to make strategic HR choices.
The co-occurrence network analysis was done with the help of 'R' software (Figure 3), which confirms the link between competitive advantage, decision-making, and firm performance.
Organizations should view HR analytics as a strategic imperative contributing to enhanced decision-making, optimized HR practices, and improved overall performance. Strategic adoption of HR analytics and continuous evaluation and adaptation can position organizations for sustained success in an evolving business landscape. By addressing ethical considerations, investing in talent, and aligning HR analytics with organizational goals, businesses can harness the full potential of HR analytics to drive positive outcomes across decision-making, HR practices, and performance.
Conclusion
With the advent of big data and technology, decision-making has come to rely more on evidence than on intuition. Minbaeva (2020) viewed HR analytics as a hammer for constructive and destructive purposes. However, according to this review, the constructive or harmful use of HR analytics depends on the organization's use of knowledge, people, skills, and resources. Organizations can look for solutions to address the issues of ethical concerns, safety and security measures, and psychological consequences of HR analytics before implementing analytics, as it will lessen the negative impact of analytics. Employees' positive psychological wellbeing enhances their productivity and effectiveness. HR analytics can also be used to keep an eye on the wellbeing of employees and alter training modules according to their requirements. This study finds empirical evidence in the literature linking HR analytics to performance.
Leveraging HR practices (i.e., recruitment and selection, performance management, training and development) efficiently yields beneficial outcomes and gives organizations a competitive advantage (Schuler and Macmillan, 1984; and Albrecht et al., 2015). The study supports the notion that HR analytics aids the management in strategic decision-making while implementing effective HR practices, which results in improved organizational performance and competitive edge.
Practical Implications and Future Scope
The practical implications of the research findings in the paper can be translated into actionable insights for organizations, HR professionals, and policymakers. The study addresses three key aspects: decision-making, HR practices, and performance.
Decision-Making Aspect
Practical Implication: Organizations should invest in HR analytics platforms and technologies to improve decision-making. This involves using business intelligence and DSS to supply accurate, fast, and dependable data to support HR decisions. Integrating algorithms, analytics, and measurements should be a top priority to reduce subjectivity in decision-making.
Action Steps
- Conduct a thorough assessment of the organization's decision-making processes.
- Invest in and implement HR analytics tools that align with organizational needs.
- Provide training for HR professionals to use analytics for data-driven decision-making.
- Establish protocols for ethical implementation and execution of HR analytics.
HR Practices and Function Aspect
Practical Implication: HR professionals should leverage analytics to optimize HR practices such as recruitment, training, retention, turnover management, and employee engagement. Using analytics in recruitment can streamline processes, reduce bias, and improve candidate selection. Training initiatives can be tailored based on predictive analytics, and employee retention strategies can be enhanced using data-driven insights.
Action Steps
- Integrate HR analytics into recruitment processes for better candidate selection.
- Utilize predictive analytics to identify training needs and optimize training programs.
- Implement retention strategies based on HR analytics insights.
Performance
Practical Implication: Organizations must recognize HR analytics as a tool that directly influences overall performance. Organizations can derive value from HR analytics by investing in data quality, analytics capabilities, and strategic abilities. Evidence-based management, supported by HR analytics, is pivotal in improving organizational performance, employee engagement, and strategic decision-making.
Actions Steps
- Develop a comprehensive HR analytics strategy aligned with organizational goals.
- Invest in analytical capabilities, including HRIS and skilled data analysts.
- Evaluate HR analytics' effect on performance measures regularly.
- Foster a culture of evidence-based decision-making at all organizational levels.
References
- Albrecht S L, Bakker A B, Gruman J A et al. (2015), "Employee Engagement, Human Resource Management Practices and Competitive Advantage: An Integrated Approach", Journal of Organizational Effectiveness: People and Performance, Vol. 1, No. 3, pp. 261-280.
- Aral S, Brynjolfsson E and Wu L (2012), "Three-way Complementarities: Performance Pay, Human Resource Analytics, and Information Technology", Management Science, Vol. 58, No. 5, pp. 913-931. https://doi.org/http://dx.doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.1110.1460
- Avrahami D, Pessach D, Singer G and Chalutz Ben-Gal H (2022), "A Human Resources Analytics and Machine-Learning Examination of Turnover: Implications for Theory and Practice", International Journal of Manpower. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJM-12-2020-0548
- Batistic S and Laken P Van Der (2019), "History, Evolution and Future of Big Data and Analytics: A Bibliometric Analysis of Its Relationship to Organizational Performance", British Journal of Management, Vol. 30, No. 2, pp. 229-251. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8551.12340
- Bechter B, Brandl B and Lehr A (2022), "The Role of Firms' Capability, Opportunity, and Motivation for using Human Resource Analytics to Monitor Employee Performance: A Multi-Level Analysis of the Organizational, Market, and Country Context", New Technology, Work and Employment, Vol. 37, No. 3, pp. 1-27. https://doi.org/10.1111/ntwe.12239
- Becker B E, Huselid M A and Beatty R W (2009), The Differentiated Workforce: Translating Talent into Strategic Impact, Harvard Business Press, Boston, MA.
- Ben-gal H C (2019), "An ROI-based Review of HR Analytics: Practical Implementation Tools", Personnel Review, Vol. 48, No. 6, pp. 1429-1448. https://doi.org/10.1108/PR-11-2017-0362
- Brown M I (2020), "Comparing the Validity of Net Promoter and Benchmark Scoring to other Commonly used Employee Engagement Metrics", Human Resource Development Quarterly, Vol. 31, No. 4, pp. 355-370. https://doi.org/10.1002/hrdq.21392
- Chowdhury S, Joel-Edgar S, Dey P K and Kharlamov A (2022), "Embedding Transparency in Artificial Intelligence Machine Learning Models: Managerial Implications on Predicting and Explaining Employee Turnover", The International Journal of Human Resource Management, Vol. 34, No. 14, pp. 2732-2764. https://doi.org/10.1080/09585192.20 22.2066981
- Cotes J and Ugarte S M (2019), "A Systemic and Strategic Approach for Training Needs Analysis for the International Bank", Journal of Business Research, May 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.05.002
- Davenport T H, Harris J and Shapiro J (2010), "Competing on Talent Analytics", Harvard Business Review. Vol. 88, No. 10, pp. 52+.
- Du L and Li Q (2019), "A Data-Driven Approach to High-Volume Recruitment: Application to Student Admission", Manufacturing & Service Operations Management, Vol. 22, No. 5, pp. 942-957.
- Dulebohn J H and Johnson R D (2013), "Human Resource Metrics and Decision Support: A Classification Framework", Human Resource Management Review, Vol. 23, No. 1, pp. 71-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2012.06.005
- Ellmer M and Reichel A (2021), "Staying close to Business: The Role of Epistemic Alignment in Rendering HR Analytics outputs Relevant to Decision-Makers Relevant to Decision-Makers", The International Journal of Human Resource Management. https://doi.org/10.1080/09585192.2021.1886148
- Elrehail H, Harazneh I, Abuhjeeleh M et al. (2020), "Employee Satisfaction, Human Resource Management Practices and Competitive Advantage: The Case of Northern Cyprus". European Journal of Management and Business Economics, Vol. 29, No. 2, pp. 125-149. https://doi.org/10.1108/EJMBE-01-2019-0001
- Frederiksen A (2017), "Job Satisfaction and Employee Turnover: A Firm-Level Perspective", German Journal of Human Resource Management, Vol. 31, No. 2, pp. 132-161. https://doi.org/10.1177/2397002216683885
- Garcia-arroyo J and Osca A (2019), "Big Data Contributions to Human Resource Management: a Systematic Review", The International Journal of Human Resource Management, Vol. 32, No. 20, pp. 4337-4362. https://doi.org/10.1080/09585192.2019.1674357
- Gurusinghe R N, Arachchige B J H and Dayarathna D (2021), "Predictive HR Analytics and Talent Management: A Conceptual Framework", Journal of Management Analytics, Vol. 8, No. 2, pp. 195-221. https://doi.org/10.1080/23270012.2021.1899857
- Hanisch B and Wald A (2008), "A Bibliometric View on the Use of Contingency Theory in Project Management Research", Project Management Journal, Vol. 43, No. 3, pp. 4-23. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmj
- Hastuti R and Timming A R (2021), "Can HRM Predict Mental Health Crises? Using HR Analytics to Unpack the Link Between Employment and Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviours", Personnel Review. https://doi.org/10.1108/PR-05-2021-0343
- Hickman L, Saef R, Ng V et al. (2021), "Developing and Evaluating Language?based Machine Learning Algorithms for inferring Applicant Personality in Video Interviews", Human Resource Management Journal, pp. 1-20. https://doi.org/10.1111/1748-8583.12356
- Holwerda J A (2021), "Big Data? Big Deal: Searching for Big Data's Performance effects in HR", Business Horizons, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2021.02.006
- Kappelman L, Mclean E, Maurer C et al. (2020), "The 2019 SIM IT Issues and Trends Study 1", MIS Quarterly Executive, 2020 (March), Vol. 19, No. 1, pp. 69-104. https:/ /doi.org/10.17705/2msqe.00026
- Kim J, Dibrell C, Kraft E and Marshall D (2021), "Data Analytics and Performance: The Moderating Role of Intuition-based HR Management in Major League Baseball ?", Journal of Business Research, Vol. 122, No. 1, pp. 204-216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.08.057
- King K G (2016), "Data Analytics in Human Resources: A Case Study and Critical Review", Human Resource Development Review, Vol. 15, No. 4, pp. 487-495. https:/ /doi.org/10.1177/1534484316675818
- Laken P Van Der, Bakk Z, Giagkoulas V et al. (2017), "Expanding the Methodological Toolbox of HRM Researchers: The added Value of Latent Bathtub Models and Optimal Matching Analysis", Human Resource Management, Vol. 57, No. 3, pp. 751-760. https:/ /doi.org/10.1002/hrm.21847
- Larsson A and Edwards M R (2021), "Insider Econometrics Meets People Analytics and Strategic Human Resource Management", The International Journal of Human Resource Management, Vol. 33, No. 12, pp. 2373-2419. https://doi.org/10.1080/ 09585192.2020.18 47166
- Levenson A (2017), "Using Workforce Analytics to Improve Strategy Execution", Human Resource Management, Vol. 57, No. 3, pp. 685-700. https://doi.org/10.1002/ hrm.21850
- Liu Y, Pant G and Sheng O R L (2020), "Predicting Labor Market Competition: Leveraging Interfirm Network and Employee Skills", Information Systems Research, Vol. 31, No. 4, pp. 1443-1466.
- Love L F and Singh P (2011), "Workplace Branding: Leveraging Human Resources Management Practices for Competitive Advantage Through "Best Employer" Surveys", Journal of Business and Psychology, Vol. 26, No. 2, pp. 175-181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10869-011-9226-5
- Margherita A (2022), "Human Resources Analytics: A Systematization of Research Topics and Directions for Future Research", Human Resource Management Review, November. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2020.100795
- Marler J H and Boudreau J W (2017) "An Evidence-Based Review of HR Analytics", International Journal of Human Resource Management, Vol. 28, No. 1, pp. 3-26. https://doi.org/10.1080/09585192.2016.1244699
- McAbee S T, Landis R S and Burke M I (2016), "Inductive Reasoning: The Promise of Big Data", Human Resource Management Review, Vol. 27, No. 2, pp. 277-290. https:/ /doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2016.08.005
- McCartney S and Fu N (2022), "Bridging the Gap: why, how and when HR Analytics can Impact Organizational Performance", Management Decision, Vol. 60, No. 13, pp. 25-47.
- Mclver D, Lengnick-hall M L and Lengnick-hall C A (2018), "A Strategic Approach to Workforce Analytics: Integrating Science and Agility", Business Horizons, Vol. 61, No. 3x, pp. 397-407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2018.01.005
- Minbaeva D (2020), "Disrupted HR? Human Resource Management Review", https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2020.100820
- Minbaeva D B (2017), "Building Credible Human Capital Analytics for Organizational Competitive Advantage", Human Resource Management, Vol. 57, No. 3, pp. 701-713. https://doi.org/10.1002/hrm.21848
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J et al. (2009), "Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement", PLoS Medicine.
- Nagpal T and Mishra M (2021), "Analyzing Human Resource Practices For Decision Making in the Banking Sector using HR Analytics", Materials Today: Proceedings. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2214785320401774
- Newman D T, Fast N J, Harmon D J et al. (2020), "When Eliminating Bias is not Fair: Algorithmic Reductionism and Procedural Justice in Human Resource Decisions", Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, Vol. 160, September, pp. 149-167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.obhdp.2020.03.008
- Pace D (2006), "Moneyball Lessons: The Transition from HR Intuition to HR Analytics", Human Resource Management, Vol. 45, No. 1, pp.140-142. https://doi.org/10.1002/hrm
- Pfeffer J and Ulrich D (2001), "Competitive Advantage through Human Resource Management: Best Practices or Core Competencies?", Human Relations, Vol. 54, No. 3, pp. 361-372. https://doi.org/10.1177/0018726701543005
- Posthumus J, Bozer G and Joseph C Santora (2018), "The use of Market Analytics in the Recruitment of High Potentials in the Pharmaceutical Industry", European Journal of International Management, Vol. 13, No. 4, pp. 496-514. https://doi.org/10.1504/EJIM.2018.10014150
- Prokesch S (2017), "Reinventing Talent Management: How GE Uses Analytics to Guide a More Digital, Far-Flung Workforce", Harvard Business Review. https://scholar.harvard.edu/people_analytics/publications/task-now-just-perform-execute-and-let-market-make-its-own
- Qamar Y and Samad T A (2022), "Human Resource Analytics: a Review and Bibliometric Analysis", Personnel Review, Vol. 51, No. 1, pp. 251-283. https://doi.org/10.1108/PR-04-2020-0247
- Rombaut E and Guerry M (2019), "The Effectiveness of Employee Retention through an Uplift Modelling Approach", International Journal of Manpower, Vol. 41, No. 8, pp. 1199-1220. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJM-04-2019-0184
- Ryan J C (2019), "Retaining, Resigning and Firing: Bibliometrics as a People Analytics Tool for Examining Research Performance Outcomes and Faculty Turnover", Personnel Review, Vol. 50, No. 5, pp. 1316-1335. https://doi.org/10.1108/PR-12-2019-0676
- Samson K and Bhanugopan R (2022), "Strategic Human Capital Analytics and Organization Performance: The Mediating Effects of Managerial Decision-Making", Journal of Business Research, Vol. 144, May, pp. 637-649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2022.01.044
- Schiemann W A, Seibert J H and Blankenship M H (2017), "Putting Human Capital Analytics to work: Predicting and Driving Business Success", Human Resource Management, Vol. 57, No. 3, pp. 795-807. https://doi.org/10.1002/hrm.21843
- Schuler R S and Macmillan I C (1984), "Gaining Competitive Advantage through Human Resource Management Practices", Human Resource Management, Vol. 23, No. 3, pp. 241-255.
- Shamim S, Zeng J, Muhammad S and Khan Z (2018), "Role of Big Data Management in Enhancing Big Data Decision-Making Capability and Quality among Chinese Firms: A Dynamic Capabilities View", Information & Management, Vol. 56, No. 6, pp. 103-135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2018.12.003
- Singh R, Sharma P, Foropon C and Belal H M (2022), "The Role of Big Data and Predictive Analytics in Employee Retention: a Resource-based View", In International Journal of Manpower, Vol. 43, No. 2, pp. 411-447. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJM-03-2021-0197
- Speer A B (2021), "Empirical Attrition Modelling and Discrimination: Balancing Validity and Group Differences", Human Resource Management Journal, Vol. 34, No. 1, pp. 1-19. https://doi.org/10.1111/1748-8583.12355.
- Strohmeier S, Collet J and Kabst R (2022), "(How) do Advanced Data and Analyses Enable HR Analytics Success? A Neo-Configurational Analysis", Baltic Journal of Management, Vol. 17, No. 3, pp. 285-303. https://doi.org/10.1108/BJM-05-2021-0188
- Thakur S J (2017), "People Analytics in the Era of Big Data: Changing how you Attract, Acquire, Develop, and Retain Talent", Personnel Psychology, Vol. 70, No. 4, pp. 929-930. https://www.webofscience.com/wos/woscc/full-record/WOS:000414335800008
- Ulrich D and Dulebohn J H (2015), "Are we there yet? What is next for HR?", Human Resource Management Review, Vol. 25, No. 2, pp. 188-204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr. 2015.01.004
- Van den Heuvel S and Bondarouk T (2017), "The Rise (and Fall?) of HR Analytics: A Study into the Future Application, Value, Structure, and System Support", Journal of Organizational Effectiveness: People and Performance, Vol. 4, No. 2, pp. 157-178. https://doi.org/10.1108/JOEPP-03-2017-0022
- Wang L and Cotton R (2017), "Beyond Moneyball to Social Capital inside and out: The Value of Differentiated Workforce Experience Ties to Performance", Human Resource Management, Vol. 57, No. 3, pp. 761-780. https://doi.org/10.1002/hrm.21856
- Wang X and Zhi J (2021), "A Machine Learning-based Analytical Framework for Employee Turnover Prediction", Journal of Management Analytics, Vol. 8, No. 3, pp. 351-370. https://doi.org/10.1080/23270012.2021.1961318
- Wright N (2017), "Gene Pease. Optimize your Greatest Asset-your People: How to apply Analytics to Big Data to Improve your Human Capital Investments", Personnel Psychology, Vol. 70, No. 3, pp. 713-715. https://doi.org/10.1111/peps.12230
- Yuan S, Kroon B and Kramer A (2021), "Building Prediction Models with Grouped Data: A Case Study on the Prediction of Turnover Intention", Human Resource Management Journal, Vol. 34, No. 1, pp. 20-38. https://doi.org/10.1111/1748-8583.12396