
April'23
The IUP Journal of Organizational Behavior
Archives
Metaverse and Future of Work: Avenues and Challenges
Swati Singh
State Aided College Teacher, Department of Women's Studies, Lady Brabourne College, Kolkata, West Bengal, India. E-mail: basuroyamrita1983@gmail.com
br>
Sita Vanka
Senior Professor, School of Management Studies, University of Hyderabad. Hyderabad, Telangana, India. E-mail: sita.vanka@uohyd.ac.in
br>
Metaverse is the next generation of the Internet that will impact the way individuals live, interact, and work. Metaverse is expected to revolutionize workplaces in the future. While there is increased discussion on the influence of metaverse at workplace, there is minimal evidence that highlights the use-cases issues, concerns, and practical problems related to the use of metaverse at work. The paper attempts to address this issue and provide an overview of definitions of the metaverse and outline the differences between traditional, contemporary, and metaverse workplaces. The paper's contribution to scholarship is made concrete through the discussion of potential avenues and use cases of metaverse at work, as well as issues and challenges delineating propositions linked to it. To this end, we discuss potential avenues of metaverse at work in training and development, collaboration and teamwork, alleviation of work alienation, and onboarding. We also discuss the issues of ergonomic and ethical considerations, along with technostress pertaining to the use of metaverse at work.
Introduction
Metaverse appears to be the most hyped word in recent times. The volume of searches for the word "metaverse" has immensely proliferated. Metaverse refers to a shared, decentralized, 3D digital world where individuals can enter, work and play. Most of the top IT organizations have bet high on this technology (e.g., Meta, Microsoft, Google, etc.) and its use is different verticals, e.g., advertising and promotions, among others. Similarly, early precursors to the impact of metaverse indicate that it may impact training and development, learning, collaboration, and communication in the workplace. As metaverse is highly scalable, real-time 3D provides synchronicity and persistence with the possibility of continuity of data, identity, and history, it presents several opportunities for the workplace as well. Early research in the area of the implication of metaverse at workplaces indicates that it can provide immersive experiences to employees. For instance, individuals in a metaverse environment can have private interactions similar to that of the physical environment as against the present way of interacting in breakout rooms while working on a virtual platform.
The early precursors and emerging research in the field of implications of the metaverse indicate that metaverse can transform the way work is done. Consequently, it is being highlighted as the environment for the future of work (Forbes, 2022). Several organizations have forayed into the metaverse domain to develop assistive and collaborative tools, e.g., Digital Twins of a Person (DToP), hybrid work support tools, and immersive training platforms (Gartner, 2022a). Such technologies and tools accrue several benefits. For instance, NextMeet, an avatar-based metaverse solution company from India, develops collaborating and learning solutions for organizations. The company aims to alleviate work alienation and isolation through metaverse platforms among individuals working remotely (Purdy, 2022). Work alienation is found to be high among employees who work from home due to several reasons including lack of communication, lack of social interaction, and estrangement from work (Kakkar et al., 2022). In that scenario, a metaverse platform where employees can create their avatars and interact with each other in a 3D-live space can boost collaboration and interaction.
Apart from collaboration and interaction, metaverse could be crucial for training and development at the workplace. Metaverse ecosystem for immersive training can be mutually beneficial for employees and employers (Upadhyay and Khandelwal, 2022). Immersive training through the metaverse platform can make training more effective, engaging, and efficient. For instance, Microsoft's HoloLens technology is being used to train workers (such as plumbers) through live visualization and gaming (Microsoft, 2022), and train medical students about human anatomy through interactive 3D models (Purdy, 2022).
It is evident that the use-cases for the implications of metaverse at work are increasing. However, most of the work in the field of metaverse and its implication on work is journalistic in nature. There is a lack of scholarly research in this area. More specifically, there are few studies which adopt a conceptual approach to studying the implications of metaverse at the workplace. At the same time, there is minimal evidence which highlights the use-cases issues, concerns and practical problems related to the use of metaverse at the workplace. This paper attempts to address this issue. In doing so, we discuss the existing definitions of metaverse. In alignment with Felix, Hinsch and Rauschnabel in Dwivedi et al. (2022), we outline potential avenues for the use of metaverse at workplaces. We also discuss issues and challenges with respect to the use of metaverse at work. Furthermore, we develop propositions with respect to the potential avenues and challenges pertaining to the use of metaverse at work.
In this paper, we aim to contribute to the emerging academic discourse on metaverse. We also attempt to respond to the call for more scholarly analysis and research in the area of metaverse "beyond the hype" (Dwivedi et al., 2022). Our contribution to the scholarship is made concrete by identifying key areas with respect to the metaverse and its implications at work and delineating key research propositions. To this end, the rest of the paper is structured as follows: first, we discuss existing definitions of metaverse; we then highlight the specific potential avenues and use cases of metaverse at the workplace; and following that, we specify the future research areas.
Metaverse - Overview and Definitions
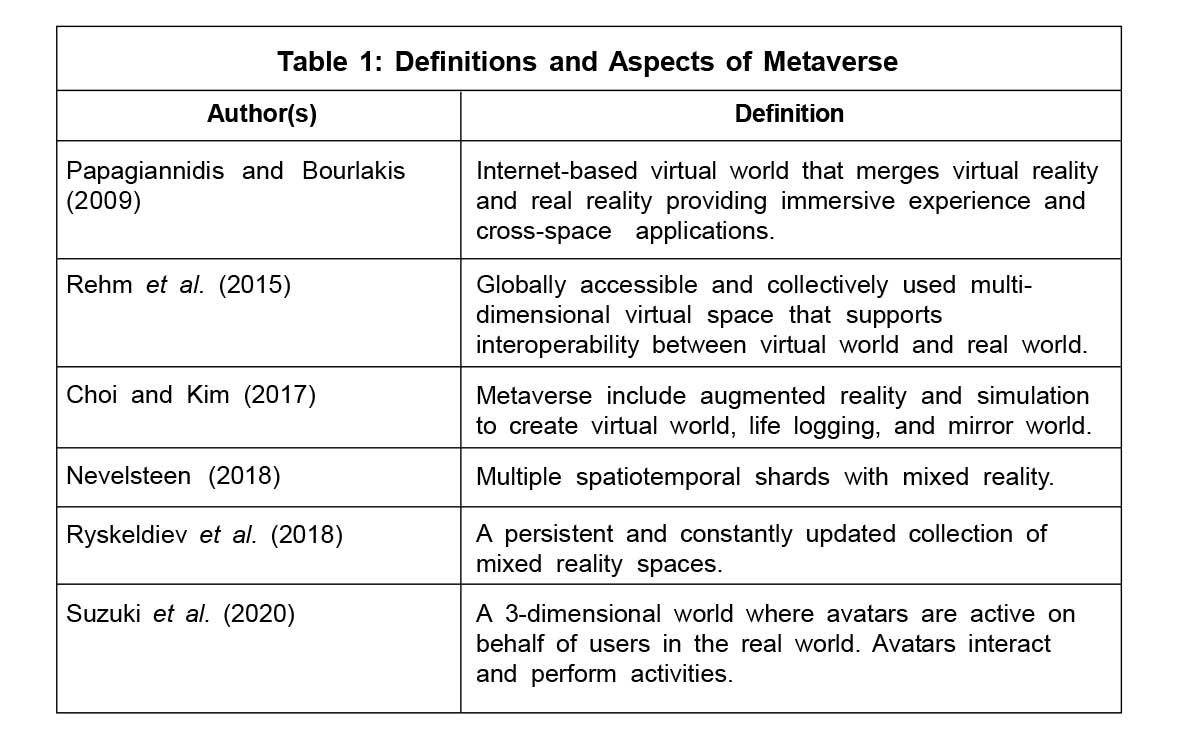
There are varied definitions of metaverse. However, most definitions point out the fact that metaverse is a virtual world that replicates the real world. The precursors of metaverse were created in Web 2.0. Today, however, with Web 3.0, metaverse combines real-time data with Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality (VR and AR) to provide reality-based immersive experiences to users. Kim and Sun Joo (Grace) Ahn (2021, p. 142) includes these advances in the definition and describes metaverse as "an interoperated persistent network of shared virtual environments where people can interact synchronously through their avatars with other agents and objects." Park and Kim in Dwivedi et al. (2022) describe four aspects of metaverse, namely, environments, interface, interaction, and social value, highlighting the dimensions of metaverse and the value it creates for the users.
There are diverse approaches and applications of metaverse. Metaverse platforms can be used as tools as well as targets (Park and Kim, 2022). Metaverse as a tool complements the tasks of real world. As a tool, it enhances efficiency by execution of tasks that are economically unviable and difficult to perform in the real world, thus finding its application at work (e.g., use of metaverse in training), education, healthcare and social life. Furthermore, the applications of metaverse as a target can also be found. Metaverse as target relates to the metaverse itself contributing to profits and generation of new metaverse platforms, unlike a tool that facilitates other processes. The application of metaverse as a target is often seen in gaming, business, and real estate (e.g., metaverse application companies can sell a region on their metaverse), among others.
Scholars have highlighted different aspects of metaverse while defining its dimensions and applications. The different definitions of metaverse indicate its evolution from a "second life" to a more immersive and persistent platform that resembles the real world.
Table 1 provides an overview of key definitions of metaverse.
Together these definitions highlight that metaverse is a merger between physical world and digital world. Metaverse exists together, parallel, and concurrent to the real, physical world. Technologies allow switching between physical and digital world providing augmented, blended, and virtual immersive experiences. Metaverse is likely to have an impact on all domains of life, and work is no exception to it.
With the advent of technology, interoperability between real and virtual world is likely. Metaverse is seen as a vehicle for shifts in cyber-physical environment in which work
is expected to be performed in future. A key question here, though, is whether and how this interoperability affects the productivity and collaboration at work. To this end, in the next section, a comparison of traditional work and work in metaverse is presented. Further, the most salient of multiple potential avenues toward applying the metaverse at work are outlined. Additionally, specific use cases of metaverse at work are also discussed.
Metaverse and Future Work
Metaverse at workplace relates to virtual reality environment that allows work from anywhere and ensures immersive experience and collaboration. Metaverse is predicted to be the most critical driver of change in technology and business evolution in coming years. A recent report highlights that "through 2027, fully virtual workspaces will account for 30% of the investment growth by enterprises in metaverse technologies and will 'reimagine' the office experience" (Gartner, 2022b, p. 2). This indicates that virtual workspaces will be a reality in near future. Moreover, it will influence the way work is carried out in the organizations and the way organizations acquire, manage and enhance human capital. With virtuality becoming a reality at work, individuals can join organizations regardless of geographic location. To employees, metaverse-driven workplace may provide an alternative to travel (when not required). Alongside, for the organizations which promote remote work and hybrid work culture, metaverse may take center stage and become the core of employee experience.
It is evident that metaverse workplaces will be distinct from the traditional workplaces and the workplace of the current times on several dimensions. Metaverse workplaces will be distinct in terms of place of work and approach, thus ensuing several benefits. However, metaverse workplaces will not be devoid of limitations. A comparison of approach, benefits, and limitations of traditional, contemporary, and metaverse workplaces is shown in Table 2.
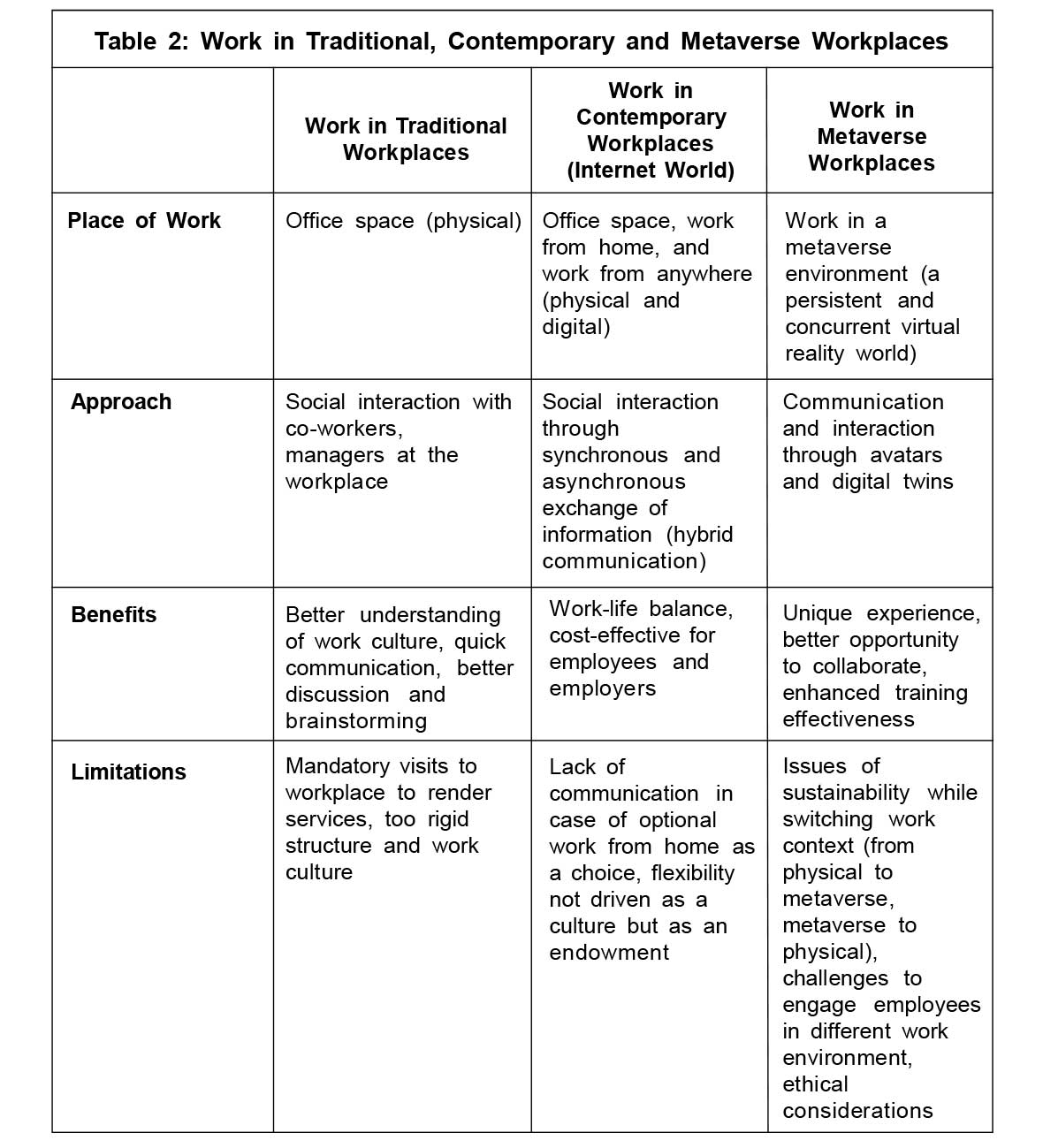
It shows that metaverse workplaces offer several benefits, but they also have certain drawbacks. As creating and maintaining a metaverse workplace could be expensive, it may still take some time before it becomes widely accepted. Employees may still be hesitant to adopt this new technology. Additionally, even in the case of adoption of metaverse at workplace, challenges with respect to employee engagement and context switching pertain.
Metaverse at Work - Potential Avenues
Adoption of metaverse at workplace is still at infancy. It is safe to surmise that currently the existing "precursor" or "pre-metaverse" solutions help in anticipating how metaverse at workplace would reshape work environment. Thus, it becomes vital to outline potential avenues signifying the specific use cases of metaverse at work. Additionally, it is also crucial to highlight the challenges pertaining to it. The most salient of several possible potential avenues are discussed below.
Collaboration and Teamwork
Collaboration and teamwork are valued in today's organization to achieve shared goals. Both collaboration and teamwork allow individuals to combine expertise and problem-solving skills. Collaboration and teamwork are reported to have a positive influence on productivity, performance, and output (McInnes et al., 2015). Effective communication and open channels of communication are the backbone of collaboration and teamwork (Driskell et al., 2018). Metaverse platforms are expected to enhance the quality of communication and provide technologically advanced platform to collaborate. For instance, Matterport, a metaverse platform development company, provides platforms that can develop digital replica of physical spaces. It helps in developing digital twin workflow that enhances collaboration and decision making (Keshavarzi et al., 2020). Metaverse can also enhance teamwork experience through the use of 3D collaboration tools, using which all team members (even if working from different places physically) can meet and work together virtually, thus enhancing communication, team bonding, experience, ideation, and relationship. Hence, it is expected that:
P1: Metaverse will facilitate both collaboration and teamwork through enhanced communication, ideation, and decision-making.
Onboarding of New Hires
Onboarding is a process through which new hires are integrated into the organization. Onboarding allows employees to socialize and gain information, knowledge, and skills to become productive and satisfied workers (Snell, 2006). Onboarding is hence crucial for familiarity with work, procedures, and organizational culture.
Employee onboarding is one area where application of metaverse can be fruitful and beneficial. Through metaverse, employees can be given immersive experience of the organization, its history, milestones, and achievements, which at present are provided through a lecture-session or audio-visual medium. Organizations have identified value in metaverse for onboarding experiences. For instance, Accenture uses metaverse for employee onboarding through its metaverse platform, nth Floor, where employees can create their avatars and interact in a 3D virtual space. Immersive experience is also enhanced by the tour of virtual campus "One Accenture Park". Hence, onboarding is one area where metaverse has important use case for organizations.
P2: Use of metaverse platforms for onboarding will enhance the onboarding experience through immersive augmented experiences.
Immersive Training Through Metaverse
Training and Development (T&D) are core functions in an organization. It aims at improving job performance, work attitudes and behaviors. T&D programs are educational activities that involve advancement of employee knowledge and skills to enhance their ability to perform their jobs in a better manner. Most of the training modules are conducted in-person or provided through audio-visual method (2D platforms). Metaverse can revolutionize the way corporate training is imparted. Metaverse can provide an opportunity to learners to experience visuals and dimensions which are not possible in 2D learning. Instead of passive information providing, organizations can provide immersive learning to employees. Use of metaverse for training can be crucial in specific scenarios such as manufacturing, medical equipment, and invasive procedures (e.g., surgery). Hence:
P3: Metaverse will enhance the effectiveness of training through immersive learning and simulation.
Addressing Work Alienation in Remote Work
Covid-19 presented an unprecedented situation where organizations had to adopt forced remote work. In the post-pandemic scenario as well, several organizations continue the remote work and many organizations are adopting hybrid work model. In remote work scenario, work alienation has been reported to be a major challenge (Kakkar et al., 2022). Work alienation is experienced by employees due to estrangement from work. The estrangement may arise due to perception of bias (Singh and Vanka, 2020), lack of communication, and lack of social interaction, among others. The feeling of estrangement is enhanced while working remotely (Kakkar et al., 2021). Work alienation is found to have a negative impact on performance, job satisfaction, and commitment (Shantz et al., 2015).
Metaverse can provide a viable solution to alleviate work alienation among employees who work remotely. Metaverse platforms provide simulating co-presence which can allow social interaction through enabling technologies. The scalability of metaverse can allow it to arrange meetings with a large number of participants akin to reality. Put simply, metaverse platforms can help alleviate estrangement in remote work scenario.
P4: Metaverse will alleviate work alienation among employees who work remotely through simulating co-presence and interaction.
The above-mentioned potential avenues highlight some of the important use cases of metaverse at workplace. Alongside use cases and benefits, there are several challenges and issues that need to be addressed while adopting metaverse at work.
Metaverse at Work - Issues and Challenges
Despite many potential benefits of using metaverse at work, issues and challenges linked to it cannot be ignored. While several challenges are being highlighted with respect to diminishing returns of using metaverse if organizations fail to reskill employees and lack effective process for its implementation and management (Paul et al., 2022), some of the key challenges are discussed below:
Ergonomic Considerations
Ergonomics is the science of fitting workplaces to user needs. It deals with designing of work in a manner that enhances productivity and reduces fatigue and severity of work, e.g., designing comfortable office furniture and creating accessible workstations, among others. Ergonomic challenges with respect to the use of metaverse at work cannot be ignored. At present, metaverse devises like headgears are required to enter 3D virtual spaces. Research suggests that a prolonged use of such devices may result in discomfort and fatigue (Pyun et al., 2022), which may hamper productivity and efficiency of employees. Hence:
P5: Prolonged use of materials and devices of metaverse may result in fatigue and discomfort that may lead to reduced productivity and performance.
Ethical Considerations
Metaverse is a persistent and concurrent virtual reality where rich data is captured through Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) tools. These data include biometric information, gestures, and facial features, among others. The magnitude of data gathered while working on metaverse raises an alarm for privacy and security concerns. Such sensitive information can be misused if not protected properly. Additionally, employees may not like continuous monitoring and tracking through metaverse platforms viewing it as a breach of privacy. Organizations may face challenges in this regard while implementing metaverse at workplaces. Hence, it is anticipated that:
P6: Firms will have more pressure to ensure employee privacy and security in the metaverse workplace, as compared to traditional workplaces.
Technostress in Metaverse
Technostress is the stress linked with the inability to adapt or cope with technology. The concept of technostress was first introduced by Brod (1982), who defined technostress as a human cost of computer revolution. Technostress highlights the dark side of technology. There are three fundamental dimensions of technostress, namely, techno-anxiety, techno-addiction and techno-strain (Brivio et al., 2018). Techno-anxiety relates to the fear and apprehension linked with the uncertainty resulting out of the use of technology. Individuals have fear with respect to the outcomes of the use of technology, e.g., what will happen if I push this button. This fear and apprehension results in techno-anxiety. Techno-addiction is another important dimension of technostress. Techno-addiction is related to the inability of an individual to disconnect from work-related technologies. Techno-addiction thus results in overwork and workaholism. Techno-strain, on the other hand, is related to the stress experienced while using a new technology. Research indicates that technostress may impact the mental health and productivity of employees (Dragano and Lunau, 2020). We argue that as metaverse is a persistent virtual world that keeps changing and demands context switching, it may result in technostress. Furthermore, stress to cope with technological advancements to work effectively in metaverse may result in technostress. Thus, it can be anticipated that:
P7: Employees will experience technostress while working in metaverse environment due to uncertainty, techno-strain, and techno-anxiety.
Conclusion
At its core, metaverse is a unified way for people and things to interact in a virtual and spatial capacity. It is a collection of virtual worlds, including the physical one. In an organizational context, whether it is writing, talking, meeting, presenting, designing or deciding, people try to convey something to an audience to connect. Metaverse will eventually be another medium for this, not replacing these things but enabling and enhancing them (Hughes, 2022). Organizations like Microsoft, Google and Apple, have recognized the power of metaverse to revolutionize the workplace and started to invest to reap the benefits from its potential. While the discussion on its influence at work is loud and clear, the issues, concerns and use cases, however, are limited. This paper attempted to address the emerging evidence to highlight the potential avenues and use cases of metaverse at work, thus contributing to the limited scholarship on the subject.
Training the employees assumes significance in this context. The pandemic has been a catalyst for adopting the online methods of training, especially while working from home. Further, with the projection of a permanent WFH or a hybrid design of work, organizations and employees are looking at solutions to extending digitally for greater productivity and learning. This implies a renewed role for the HRD function in terms of training relevance, greater investment from the organizations and a bigger market for metaverse, thus requiring scholarly focus on the training methodology and its impact on the learning of employees, and new formulae to measure productivity.
Further, the absence of socialization in working from home underscores its impact on work alienation and stress, thus affecting employee health and wellbeing. The psychological implications arising out of technostress, assume a critical domain of investigation on the use of metaverse.
The use of technology has raised concerns of not only privacy and security for quite long, but ethics as well, considering the use of metaverse. Employee experience working from home demonstrates a dislike for working in a virtual environment for longer duration, apprehensions about the new technology, their exhaustion from WFH and online communication. The uncertainty caused by the pandemic has accentuated this, calling for an insightful investigation into the use of metaverse.
In summary, the pandemic and the resulting uncertainty has forced organizations towards technological innovation in the use of metaverse, thus making it an imperative in the near future. However, an integrated approach is needed to build the metaverse to make it a meaningful reality.
References
- Brivio E, Gaudioso F, Vergine I et al. (2018), "Preventing Technostress Through Positive Technology", Frontiers in Psychology, Vol. 9, https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02569
- Brod C (1982), "Managing Technostress: Optimizing the Use of Computer Technology", Personnel Journal, Vol. 61, No. 10, pp. 753-757.
- Choi H and Kim S (2017), "A Content Service Deployment Plan for Metaverse Museum Exhibitions-Centering on the Combination of Beacons and HMDs", International Journal of Information Management, Vol. 37, No. 1 (Part B), pp. 1519-1527, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2016.04.017
- Dragano N and Lunau T (2020), "Technostress at Work and Mental Health: Concepts and Research Results", Current Opinion in Psychiatry, Vol. 33, No. 4, p. 407, https://doi.org/10.1097/YCO.0000000000000613
- Driskell J E, Salas E and Driskell T (2018), "Foundations of Teamwork and Collaboration", American Psychologist, Vol. 73, No. 4, pp. 334-348, https://doi.org/10.1037/amp0000241
- Dwivedi Y K, Hughes L, Baabdullah A M et al. (2022a), "Metaverse Beyond the Hype: Multidisciplinary Perspectives on Emerging Challenges, Opportunities and Agenda for Research, Practice and Policy", International Journal of Information Management, Vol. 66, No. C, p. 102542, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2022.102542
- Dwivedi Y K, Hughes L, Wang Y et al. (2022b), "Metaverse Marketing: How the Metaverse Will Shape the Future of Consumer Research and Practice", Psychology & Marketing, Vol. 40, No. 4, pp. 750-776, https://doi.org/10.1002/mar.21767
- Forber (2022), "Why the Future of Work Could Take Place in the Metaverse", forbes.com
- Gartner (2022a), "Top Strategic Predictions for 2023 and Beyond", Gartner. Accessed on January 4, 2023.
- Gartner (2022b), "What Is a Metaverse?", gartner.com
- Hughes Ian (2022), "The Metaverse: Is It the Future?", ITNOW, Vol. 64, No. 1, pp. 22-23, https://doi.org/10.1093/itnow/bwac011
- Kakkar S, Kuril S, Singh S, Saha S and Dugar A (2021), "Influence of Communication Satisfaction and CSR Association on Job Satisfaction and Work Alienation", Academy of Management Proceedings, 2021, Vol. 1, p.14389, https://doi.org/10.5465/AMBPP.2021.14389abstract
- Kakkar S, Kuril S, Singh S, Saha S and Dugar A (2022), "The Influence of Remote Work Communication Satisfaction and CSR Association on Employee Alienation and Job Satisfaction: A Moderated-Mediation Study", Information Technology & People, (ahead-of-print), https://doi.org/10.1108/ITP-01-2021-0030
- Keshavarzi M, Yang A Y, Ko W and Caldas L (2020), "Optimization and Manipulation of Contextual Mutual Spaces for Multi-User Virtual and Augmented Reality Interaction", 2020 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces (VR), pp. 353-362, https://doi.org/10.1109/VR46266.2020.00055
- Jooyoung Kim and Sun Joo (Grace) Ahn (2022), Cited in Yogesh Dwivedi et. al., "Metaverse Marketing: How the Metaverse will Shape the Future of Consumer Research and Practice", Psychology and Marketing, Vol. 40, No. 4, pp. 750-776.
- McInnes S, Peters K, Bonney A and Halcomb E (2015), "An Integrative Review of Facilitators and Barriers Influencing Collaboration and Teamwork Between General Practitioners and Nurses Working in General Practice", Journal of Advanced Nursing, Vol. 71, No. 9, pp. 1973-1985.
- Nevelsteen K J L (2018), "Virtual World, Defined from a Technological Perspective, and Applied to Video Games, Mixed Reality and the Metaverse", Computer Animation and Virtual Worlds, Vol. 29, No. 1, p. e1752, https://doi.org/10.1002/cav.1752
- Papagiannidis S and Bourlakis M (2009), "Staging the New Retail Drama: At a Metaverse Near You!", Journal for Virtual Worlds Research, Vol. 2, No. 5, Article 5. https://doi.org/10.4101/jvwr.v2i5.808
- Park S M and Kim Y G (2022), "A Metaverse: Taxonomy, Components, Applications, and Open Challenges", IEEE Access, Vol. 10, pp. 4209-4251, https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3140175
- Paul S, Yuan L, Jain H, Robert L, Spohrer J and Lifshitz-Assaf H (2022), "Intelligence Augmentation: Human Factors in AI and Future of Work", AIS Transactions on Human-Computer Interaction, Vol. 14, No. 3, pp. 426-445, https://doi.org/10.17705/1thci.00174
- Purdy M (2022), "How the Metaverse Could Change Work", Harvard Business Review, April 5, https://hbr.org/2022/04/how-the-metaverse-could-change-work
- Pyun K R, Rogers J A and Ko S H (2022), "Materials and Devices for Immersive Virtual Reality", Nature Reviews Materials, Vol. 7, No. 11, pp. 841-843, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-022-00501-5
- Rehm S V, Goel L and Crespi M (2015), "The Metaverse as Mediator Between Technology, Trends, and the Digital Transformation of Society and Business", Journal For Virtual Worlds Research, Vol. 8, No. 2, Article 2, https://doi.org/10.4101/jvwr.v8i2.7149
- Ryskeldiev B, Ochiai Y, Cohen M and Herder J (2018), "Distributed Metaverse: Creating Decentralized Blockchain-based Model for Peer-to-Peer Sharing of Virtual Spaces for Mixed Reality Applications", Proceedings of the 9th Augmented Human International Conference, pp. 1-3, https://doi.org/10.1145/3174910.3174952
- Shantz A, Alfes K, Bailey C and Soane E (2015), "Drivers and Outcomes of Work Alienation: Reviving a Concept", Journal of Management Inquiry, Vol. 24, No. 4, pp. 382-393, https://doi.org/10.1177/1056492615573325
- Singh S and Vanka S (2020), "Workplace Flexibility Bias and Intention to Leave Among Women in IT Sector: A Parallel Mediation Model of Negative Work to Family Spill Over and Work Alienation?", https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op= view_citation&hl=en&user=JlrG5wEAAAAJ&citation_for_view=JlrG5wEAAAAJ:3fE2 CSJIrl8C??????????
- Snell A (2006), "Researching Onboarding Best Practice: Using Research to Connect Onboarding Processes with Employee Satisfaction", Strategic HR Review, Vol. 5, No. 6, pp. 32-35, https://doi.org/10.1108/14754390680000925
- Suzuki S, Kanematsu H, Barry D M et al. (2020), "Virtual Experiments in Metaverse and their Applications to Collaborative Projects: The Framework and Its Significance", Procedia Computer Science, Vol. 176, pp. 2125-2132, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2020.09.249
- Upadhyay A K and Khandelwal K (2022), "Metaverse: The Future of Immersive Training", Strategic HR Review, Vol. 21, No. 3, pp. 83-86, https://doi.org/10.1108/SHR-02-2022-0009
- Virtual Masters of Their Trade: How HoloLens is Helping Training Providers up their Game - New Zealand News Center (microsoft.com)