Sep'18
The IUP Journal of Entrepreneurship Development
Archives
Identifying the Entrepreneurial Determinants and Problems Faced by Women Entrepreneurs in Madurai District, Tamil Nadu
V Suresh Babu
Assistant Professor,
PG & Research Department of Commerce,
Mannar Thirumalai Naicker College,
Pasumalai, Madurai 625004, Tamil Nadu, India.
E-mail: nithyasureshbabu5@gmail.com
The objective of the study is to identify the major problems faced by women entrepreneurs in Madurai district, Tamil Nadu. The objective also includes identifying the key determinants contributing to women's decision to be an entrepreneur. The study covers a period of one year from June 2016 to April 2017. The primary data was collected through survey method using a schedule. Direct personal interview and telephone interview method was administered on the sample respondents. The findings reveal that earning livelihood, followed by the desire to be a successful role model and self-sufficiency are the major factors that determine choosing entrepreneurship by women in Madurai district. On the other hand, excessive burden of work, excessive tension, and health problems are found to be the major problems faced by women in taking up entrepreneurship in Madurai district.
Introduction
Women entrepreneurship has been recognized as an important source of economic growth. 'High potential' women entrepreneurs are those who through job creation and widening of markets can boost economic growth. Women entrepreneurs create new jobs for themselves and others and also provide the society with different solutions to management, organization and business problems. There are several schemes of the government at central and state level, which provide assistance for setting up training-cum-income generating activities for needy women to make them economically independent. However, they still represent a minority of the entrepreneurs. For many women entrepreneurs, access to external funds and business networking remain major challenges to growth.
The challenges and opportunities provided to the women of digital era are growing rapidly, so the job seekers are turning into job creators. They are flourishing as designers, interior decorators, exporters, publishers, garment manufacturers and still exploring new avenues of economic participation. Although the number is still small as compared to businesses owned by men, this is encouraging as it shows that women no longer adhere to the stereotype that only men can be wage earners in the family. Besides numerous obligations assigned to women like childcare and doing household chores, they can find success through their own businesses. Against this backdrop, the present study tries to identify the factors influencing the choice of women entrepreneurship and the problems faced by them.
Literature Review
Mahaboob (2013) showed that 43% of the respondents opined that their life partner (husband) had supported them a lot to become an entrepreneur, whereas 26% of the respondents opined that it was their own decision to become an entrepreneur. Further, 19% of the respondents opined that they were motivated by parents, while the remaining 12% were motivated by friends and others.
Subhash and Arora (2013) showed that women entrepreneurs face a number of obstacles during start-up stage and running up of their enterprise. These obstacles need to be addressed so that women can make significant contribution to sustained economic development and social progress of the country. This study tries to examine the financial problems faced by women entrepreneurs in Haryana during the start-up stage and running of their enterprises. The study shows the lack of adequate information about the schemes of financial institutions for women entrepreneurs and reluctance of officials to finance women entrepreneurs as the main problems faced.
Upadhye (2012) concluded that self-confidence, self-esteem, educational level and knowledge make them handle different tasks in life. Male dominance over women should change. There should be support from government, institutions and agencies to encourage women entrepreneurs. Already there are certain schemes for women entrepreneurs, but these schemes should be properly implemented and made familiar so that they can use every scheme.
Syed (2011) suggested that family support, social ties and internal motivation have positive and significant effect on the success of women entrepreneurs in the small business. The survey result also showed that women entrepreneurs face certain problems when they enter the business. The implications are discussed along with some recommendations.
Objective
The study aims to:
- Identify the factors influencing the choice of women entrepreneurship; and
- Identify the problems faced by women entrepreneurs.
Data and Methodology
The study is based on survey method. Survey was conducted on a sample of 100 respondents. This study uses both primary and secondary data. The study adopts simple random sampling technique for collecting the primary data. The primary data was collected through a well-structured schedule (see Appendix). Direct personal interview and telephone interview method was administered on the sample respondents. Secondary data was collected from various journals such as Indian journals on marketing, Kissan World, Southern Economist, and from various websites. The study covers a period of one year from June 2016 to April 2017. The tools used for data analysis are Garret's ranking and intensity value.
Results and Discussion
Factors Influencing Women Entrepreneurship
There are two factors which influence women entrepreneurs in India:
- Pull Factors: They are the factors which encourage women to become entrepreneurs. They include the desire to do something new in life for becoming self-dependent, availability of finance, concessions and subsidies.
- Push Factors: They are the factors which compel a woman to become an entrepreneur. They include financial difficulties, responsibility of the family, unfortunate circumstances like death of the husband or father, divorce, etc. However, the influence of these factors on women in becoming entrepreneur is lower than the former factors, and such requirements are either absent or found negligibly in a woman.
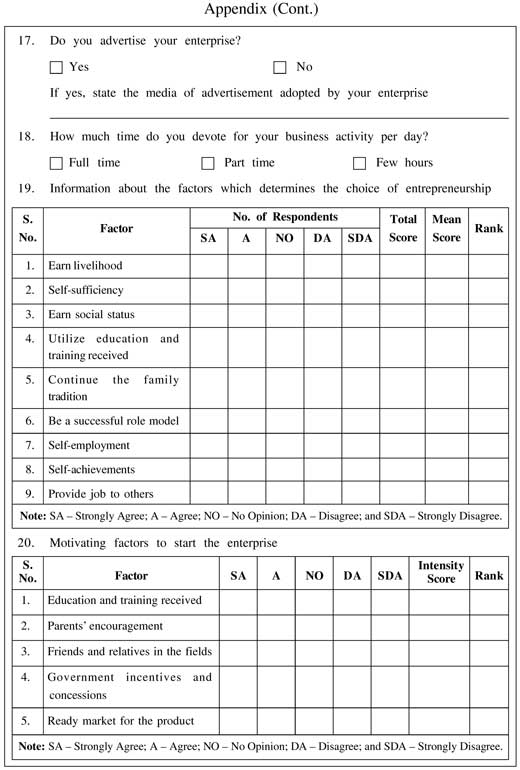
It is observed from Table 1 that on the basis of ranks given by the respondents, earning livelihood is a major factor that determines choosing entrepreneurship with the highest Garret's score of 7,081. This is followed by the factor 'to be a successful role model' that
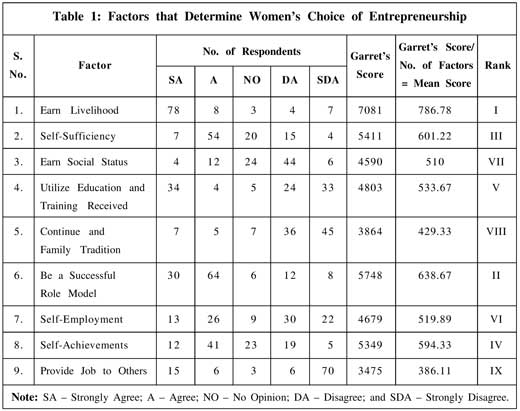
occupies the second position with the Garret's score of 5,748. Self-sufficiency is the third important factor determining the choice of entrepreneurship with the Garret's score of 5,411, followed by self-achievement (5,349), utilize education and training received (4,803), self-employment (4,679), earn social status (4590), continue the family tradition (3,864), and provide job to others (3,475).
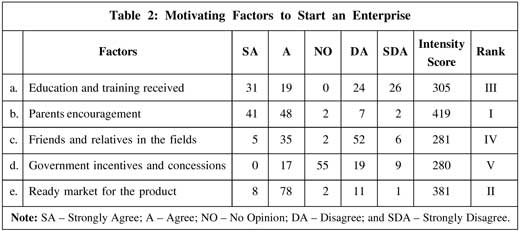
On the basis of scores given by the respondents regarding the motivating factors, it is observed from Table 2 that parents' encouragement is the most important motivating factor in starting the enterprise with the highest intensity score of 419. Ready market for the product stands at the second position with the intensity score of 381, followed by education and training received in the third position with the intensity score of 305, friends and relatives in the field in the fourth position (281) and government incentives and concessions in the fifth position (280).
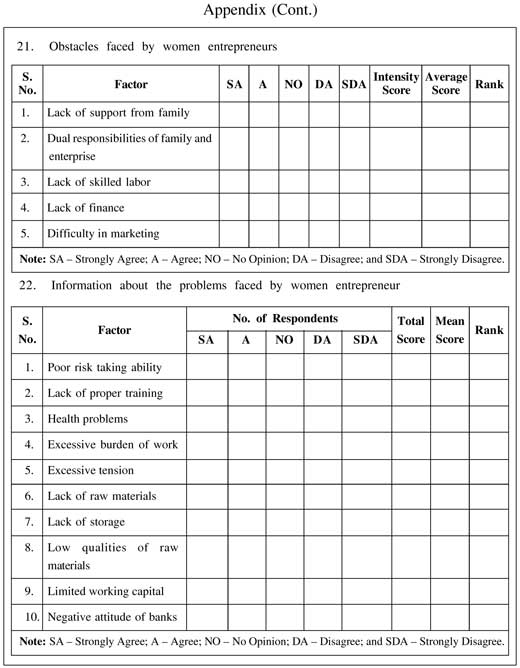
Regarding the obstacles faced by women entrepreneurs, it is observed from Table 3 that on the basis of the scores given by the respondents, 'dual responsibilities of family and enterprise' is most weighted with an intensity score of 470. Lack of finance stands at the
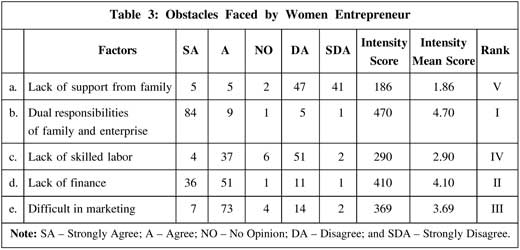
second position with the score of 410, followed by difficulty in marketing (369), lack of skilled labor (290), and lack of support from family (186).
Problems Faced by Women Entrepreneurs
Some of the major problems faced by women entrepreneurs have been identified as follows:
- Ambition, independence and autonomy are the basic ingredients required to be an entrepreneur. Such requirements are found in very few women.
- Due to low female literacy rate, women remain unaware of the technological developments, marketing trends, political skills, etc.
- Equal treatment to men and women is absent at family and social level.
- Lack of information needed to achieve entrepreneurial success.
- Women suffer due to inadequate financial resources.
- A woman is mainly subjected to a protected life throughout her lifetime, and as a result she develops lack of confidence, mobility and inferiority complex, and thus, gets easily disheartened by failure.
Based on the ranks given by the respondents as observed from Table 4, the main problem faced by women entrepreneurs with the highest Garret's score (7053) is 'excessive burden of
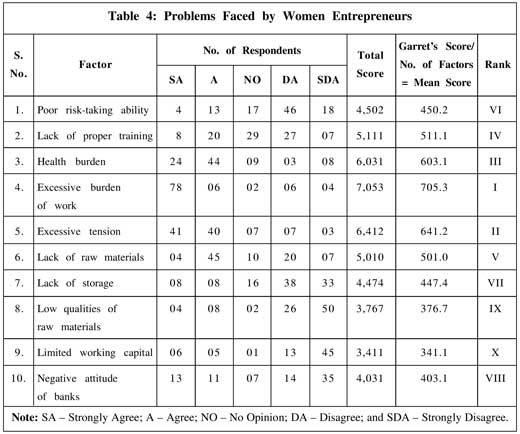
work'. Excessive tension stands at the second position with the Garret's score of 6,412, followed by health problems at third position (6,031), lack of proper training (5,111), lack of raw materials (5,010), poor risk-taking abilities (4,502), lack of storage (4,474), negative attitude of banks (4,031), low quality raw materials (3,767), and limited working capital (3,411).
Conclusion
The study is meant to be a modest beginning of research on the status and role of women entrepreneurship in Madurai district. Women entrepreneurship must be recognized for its great importance for the country's future economic prosperity. Individually, business ownership provides women with financial independence and social satisfaction. The findings reveal that women are not into business only for survival but to satisfy their inner urge of creativity and to prove their capabilities, and in this way they contribute to a great extent to social transformation. Earning livelihood, followed by the desire to be a successful role model and self-sufficiency are observed to be the first three major factors that determine choosing entrepreneurship by women in Madurai district. Further, parents' encouragement, ready market for the product and education and training received are found to be the three most important motivating factors in starting their own enterprise. Regarding the obstacles faced by women entrepreneurs, the findings reveal that dual responsibilities of family and enterprise, lack of finance and difficulty in marketing are the major obstacles. Finally, excessive burden of work, excessive tension, and health problems are found to be the major problems for women in taking up entrepreneurship in Madurai district. Thus, it can be inferred that besides supplementing their family income, the women take up entrepreneurship to improve their social/familial status and become self-sufficient. The researchers suggest that a conducive environment is the need of the hour to promote the necessary skills of women, thereby enhancing their competitiveness in the market.
Suggestions
Thus, based on the findings of the study, the following suggestions are made:
- Adequate arrangements have to be made for the supply of credit facility to women entrepreneurs.
- Access to modern machines, skills and training in the area of economically viable projects should be made available to potential women entrepreneurs.
- The government should organize special entrepreneurial development programs for rural women.
- The government should provide marketing facilities to women entrepreneurs to sell their products.
- Steps such as providing special privileges, dedicated corridors for women empowerment, etc., which are already on the paper, need to be meticulously implemented.
Limitations: This study, limited to women entrepreneurs in Madurai district, is comprehensive in nature, covering many facets of women entrepreneurship in the Madurai district. However, the scope of the study is restricted to only those women entrepreneurs who were available to be interviewed in person.
References
- Mahaboob Basha A M (2013), "A Study on the Development of Women Entrepreneurship in Nellore, AP, India", Research Journal of Management Sciences, Vol. 2, No. 10, pp. 1-5.
- Manickavasagam V Kasthuri and Jayanthi P (2007), "Women Entrepreneurs: An Analysis", Sothern Economist, Vol. 24, No. 12, p. 43.
- Sharma K K and Basotia G R (1999), Entrepreneurship and Small Business, Mangal Deep Publications, Jaipur, India.
- Subhash Chander and Arora D D (2013), "Study of Financial Problems of Women Entrepreneurs", International Journal of Social Science & Interdisciplinary Research, Vol. 2, No. 4, pp. 103-121.
- Syed Shah Alam (2011), "An Empirical Study of Success Factors of Women Entrepreneurs in Southern Region in Malaysia", International Journal of Economics and Finance, Vol. 3, No. 2, pp. 166-175.
- Upadhye Jayashree (2012), "Entrepreneurship Among Poverty Riden Women: The Confidence Building Index", International Journal of Trade, Economics and Finance, Vol. 3, No. 2.